Ziwei Shi, Xiaoran Zhang, Wenjing Xu, Yan Xia, Yu Zang, Siqi Shen, Cheng Wang
L2RSI: Cross-view LiDAR-based Place Recognition for Large-scale Urban Scenes via Remote Sensing Imagery
NeurIPS 2025, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex
xx

Ziwei Deng, Mian Deng, Chenjing Liang, Zeming Gao, Chennan Ma, Chenxing Lin, Haipeng Zhang, Songzhu Mei, Siqi Shen*, Cheng Wang
PlanU: Large Language Model Reasoning through Planning under Uncertainty
NeurIPS 2025, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex
xx

Yidong Chen, Qi Li, Yuyang Yang, Wen Li, Sheng Ao, Cheng Wang*
Unleashing the Power of Data Generation in One-Pass Outdoor LiDAR Localization
ACM MM 2025, CCF-A
 bibtex
bibtex

Yuyang Yang, Wen Li, Sheng Ao, Qingshan Xu, Shangshu Yu, Yu Guo, Yin Zhou, Siqi Shen, Cheng Wang
RALoc: Enhancing Outdoor LiDAR Localization via Rotation Awareness
ICCV 2025, Highlight, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex
xx

Haoyuan Qin, Zhengzhu Liu, Chenxing Lin, Chennan Ma, Songzhu Mei, Siqi Shen*, Cheng Wang
GradPS: Resolving Futile Neurons in Parameter Sharing Network for Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
ICML 2025, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex
xxx

Zheng Wang, Zihui Wang, Zheng Wang, Xiaoliang Fan, Cheng Wang*
Federated Learning with Domain Shift Eraser
CVPR-25 (CCF A类会议)
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{wang2025federated,
title={Federated Learning with Domain Shift Eraser},
author={Wang, Zheng and Wang, Zihui and Fan, Xiaoliang and Wang, Cheng},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2503.13063},
year={2025}
}

Zheng Wang, Wanwan Wang, Yimin Huang, Zhaopeng Peng, Ziqi Yang, Cheng Wang, Xiaoliang Fan*
P4GCN: Vertical Federated Social Recommendation with Privacy-Preserving Two-Party Graph Convolution Network
WWW-25 (CCF A类会议)
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{wang2024p4gcn,
title={P4GCN: Vertical Federated Social Recommendation with Privacy-Preserving Two-Party Graph Convolution Networks},
author={Wang, Zheng and Wang, Wanwan and Huang, Yimin and Peng, Zhaopeng and Yang, Ziqi and Wang, Cheng and Fan, Xiaoliang},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.13905},
year={2024}
}

Guiyu Zhao1️⃣, Sheng Ao1️⃣, Ye Zhang, Kai Xu, Yulan Guo
Progressive Correspondence Regenerator for Robust 3D Registration
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)
 bibtex
bibtex
@inproceedings{regor,
title={Progressive Correspondence Regenerator for Robust 3D Registration},
author={Ao, Sheng and Zhao, Guiyu and Zhang, Ye and Xu, Kai and Guo, Yulan},
booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition},
year={2025}
}

Yixin Zhang1️⃣, Sheng Ao1️⃣, Ye Zhang, Zhuo Song, Qingyong Hu, Tao Chang, Yulan Guo
U2Frame: A Unified and Unsupervised Learning Framework for LiDAR-based Loop Closing
IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA)
 bibtex
bibtex
@inproceedings{U2Frame,
title={U2Frame: A Unified and Unsupervised Learning Framework for LiDAR-based Loop Closing},
author={Ao, Sheng and Zhang, Yixin and Zhang, Ye and Song, Zhuo and Hu, Qingyong and Chang, Tao and Guo, Yulan},
booktitle={IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation)},
year={2025},
}

Chao Li, Ziwei Deng, Chenxing Lin, Wenqi Chen, Yongquan Fu, Weiquan Liu, Chenglu Wen, Cheng Wang, Siqi Shen*
DoF: A Diffusion Factorization Framework for Offline Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
ICLR 25, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex
xxx

Dunqiang Liu, Shujun Huang, Wen Li, Siqi Shen, Cheng Wang
Text to Point Cloud Localization with Multi-Level Neagtive Contrastive Learning
AAAI 2025, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex
xxx

Zijun Li, zhipeng cai, Bochun Yang, Xuelun Shen, Siqi Shen, Xiaoliang Fan, Michael Paulitsch, Cheng Wang
ConDo: Continual Domain Expansion for Absolute Pose Regression
AAAI 2025, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex
xx

Shijun Zheng, Weiquan Liu, Yu Guo, Yu Zang, Siqi Shen, Cheng Wang
A New Adversarial Perspective for LiDAR-based 3D Object Detection
AAAI 2025, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex
xxx

Zihui Wang, Zhaopeng Peng, Xiaoliang Fan*, Zheng Wang, Shangbin Wu, Rongshan Yu, Peizhen Yang, Chuanpan Zheng, Cheng Wang
FedAVE: Adaptive Data Value Evaluation Framework for Collaborative Fairness in Federated Learning
Neurocomputing
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{wang2024fedave,
title={FedAVE: Adaptive data value evaluation framework for collaborative fairness in federated learning},
author={Wang, Zihui and Peng, Zhaopeng and Fan, Xiaoliang and Wang, Zheng and Wu, Shangbin and Yu, Rongshan and Yang, Peizhen and Zheng, Chuanpan and Wang, Cheng},
journal={Neurocomputing},
volume={574},
pages={127227},
year={2024},
publisher={Elsevier}
}

Ziqi Yang, Zhaopeng Peng, Zihui Wang, Jianzhong Qi, Chaochao Chen, Weike Pan, Chenglu Wen, Cheng Wang, Xiaoliang Fan*
Federated Graph Learning for Cross-Domain Recommendation
NeurIPS-24 (CCF A类会议)
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{yang2024federated,
title={Federated Graph Learning for Cross-Domain Recommendation},
author={Yang, Ziqi and Peng, Zhaopeng and Wang, Zihui and Qi, Jianzhong and Chen, Chaochao and Pan, Weike and Wen, Chenglu and Wang, Cheng and Fan, Xiaoliang},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.08249},
year={2024}
}

KeZheng Xiong, Haoen Xiang, Qingshan Xu, Chenglu Wen, Siqi Shen, Jonathan Li, Cheng Wang
Mining and Transferring Feature-Geometry Coherence for Unsupervised Point Cloud Registration
NeurIPS 2024, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex
todo

Haoyuan Qin, Chennan Ma, Mian Deng, Zhengzhu Liu, Songzhu Mei, Xinwang Liu, Cheng Wang, Siqi Shen
The Dormant Neuron Phenomenon in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Value Factorization
NeurIPS 2024, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex
todo

Yudi Dai, Zhiyong Wang, Xiping Lin, Chenglu Wen, Lan Xu, Siqi Shen, Yuexin Ma, Cheng Wang
HiSC4D: Human-centered interaction and 4D Scene Capture in Large-scale Space Using Wearable IMUs and LiDAR
PAMI, CCF A, 2024
 bibtex
bibtex
to appear

Yitai Lin, Zhijie Wei, Wanfa Zhang, Xiping Lin, Yudi Dai, Chenglu Wen, Siqi Shen, Lan Xu, Cheng Wang
HmPEAR: A Dataset for Human Pose Estimation and Action Recognition
MM 2024, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex
...

Youliang Chu , Ming Cheng*, Zhiyang Lu , Zhentao Xiong, and Cheng Wang
Multilevel Interactive Enhanced Network for Infrared Small-Target Detection
IEEE GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING LETTERS
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{chu2024multilevel,
title={Multilevel Interactive Enhanced Network for Infrared Small Target Detection},
author={Chu, Youliang and Cheng, Ming and Lu, Zhiyang and Xiong, Zhentao and Wang, Cheng},
journal={IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters},
year={2024},
publisher={IEEE}
}

Zhaopeng Peng, Xiaoliang Fan*, Cheng Wang, et al.
FedPFT: Federated Proxy Fine-Tuning of Foundation Models
IJCAI-24 (CCF A类会议)
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{peng2024fedpft,
title={FedPFT: Federated Proxy Fine-Tuning of Foundation Models},
author={Peng, Zhaopeng and Fan, Xiaoliang and Chen, Yufan and Wang, Zheng and Pan, Shirui and Wen, Chenglu and Zhang, Ruisheng and Wang, Cheng},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.11536},
year={2024}
}

Zihui Wang, Cheng Wang, Xiaoliang Fan*, et al.
FedSAC: Dynamic Submodel Allocation for Collaborative Fairness in Federated Learning
KDD-24 (CCF A类会议)
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{wang2024fedsac,
title={FedSAC: Dynamic Submodel Allocation for Collaborative Fairness in Federated Learning},
author={Wang, Zihui and Wang, Zheng and Lyu, Lingjuan and Peng, Zhaopeng and Yang, Zhicheng and Wen, Chenglu and Yu, Rongshan and Wang, Cheng and Fan, Xiaoliang},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.18291},
year={2024}
}

Zihui Wang, Peizhen Yang, Xiaoliang Fan*, Cheng Wang, et al.,
ConTIG: Continuous Representation Learning on Temporal Interaction Graphs
Neural Networks
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{wang2024contig,
title={Contig: Continuous representation learning on temporal interaction graphs},
author={Wang, Zihui and Yang, Peizhen and Fan, Xiaoliang and Yan, Xu and Wu, Zonghan and Pan, Shirui and Chen, Longbiao and Zang, Yu and Wang, Cheng and Yu, Rongshan},
journal={Neural Networks},
volume={172},
pages={106151},
year={2024},
publisher={Elsevier}
}

Chuanpan Zheng, Xiaoliang Fan*, Cheng Wang, et al.
Spatio-Temporal Joint Graph Convolutional Networks for Traffic Forecasting
IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering (CCF A类期刊, ESI高被引论文)
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{zheng2023spatio,
title={Spatio-temporal joint graph convolutional networks for traffic forecasting},
author={Zheng, Chuanpan and Fan, Xiaoliang and Pan, Shirui and Jin, Haibing and Peng, Zhaopeng and Wu, Zonghan and Wang, Cheng and Philip, S Yu},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering},
year={2023},
publisher={IEEE}
}

Shaoyang Chen, Bochun Yang, Yan Xia, Ming Cheng, Siqi Shen, Cheng Wang*
Bridging LiDAR Gaps: A Multi-LiDARs Domain Adaptation Dataset for 3D Semantic Segmentation
IJCAI 2024, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex
xx

Weiquan Liu, Minghao Liu, Shijun Zheng, Siqi Shen, Xuesheng Bian, Yu Zang, Ping Zhong, Cheng Wang
Interpreting Hidden Semantics in the Intermediate Layers of 3D Point Cloud Classification Neural Network
TMM 2024, CCF B
 bibtex
bibtex
tmp

Zhimin Yuan, Wankang Zeng, Yanfei Su, Weiquan Liu, Ming Cheng*, Yulan Guo, Cheng Wang
Density-guided Translator Boosts Synthetic-to-Real Unsupervised Domain Adaptive Segmentation of 3D Point Clouds
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2024
 bibtex
bibtex
@inproceedings{
anonymous2024densityguided,
title={Density-guided Translator Boosts Synthetic-to-Real Unsupervised Domain Adaptive Segmentation of 3D Point Clouds},
author={Zhimin Yuan, Wankang Zeng, Yanfei Su, Weiquan Liu, Ming Cheng*, Yulan Guo, Cheng Wang },
booktitle={Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2024},
year={2024},
}

Wankang Zeng, Ming Cheng*, Zhimin Yuan, Wei Dai, Youming Wu, Weiquan Liu, Cheng Wang
Domain adaptive remote sensing image semantic segmentation with prototype guidance
Neurocomputing
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{zeng2024domain,
title={Domain adaptive remote sensing image semantic segmentation with prototype guidance},
author={Zeng, Wankang and Cheng, Ming and Yuan, Zhimin and Dai, Wei and Wu, Youming and Liu, Weiquan and Wang, Cheng},
journal={Neurocomputing},
pages={127484},
year={2024},
publisher={Elsevier}
}

Ming Yan, Yan Zhang, Shuqiang Cai, Shuqi Fan, Xincheng Lin, Yudi Dai, Siqi Shen*, Chenglu Wen, Lan Xu, Yuexin Ma, Cheng Wang
RELI11D: A Comprehensive Multimodal Human Motion Dataset and Method
CVPR 2024, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex
https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content/CVPR2024/html/Yan_RELI11D_A_Comprehensive_Multimodal_Human_Motion_Dataset_and_Method_CVPR_2024_paper.html

Zhimin Yuan, Wankang Zeng, Yanfei Su, Weiquan Liu, Ming Cheng*, Yulan Guo, Cheng Wang*
Density-guided Translator Boosts Synthetic-to-Real Unsupervised Domain Adaptive Segmentation of 3D Point Clouds
CVPR 2024
 bibtex
bibtex

Xiaotian Sun, Qingshan Xu, Xinjie Yang, Yu Zang, Cheng Wang*
Global and Hierarchical Geometry Consistency Priors for Few-shot NeRFs in Indoor Scenes
CVPR 2024
 bibtex
bibtex

Jinyi Zhang, Qihong Mao, Siqi Shen, Guosheng Hu, Cheng Wang
Neighborhood-enhanced 3D Human Pose Estimation with Monocular LiDAR in Long-range Outdoor Scenes
AAAI 2024, Oral, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex
todo

Chuanpan Zheng, Xiaoliang Fan, Cheng Wang*, Jianzhong Qi, et al.
INCREASE: Inductive Graph Representation Learning for Spatio-Temporal Kriging
WWW-23 (CCF A类会议)
 bibtex
bibtex
@inproceedings{zheng2023increase,
title={Increase: Inductive graph representation learning for spatio-temporal kriging},
author={Zheng, Chuanpan and Fan, Xiaoliang and Wang, Cheng and Qi, Jianzhong and Chen, Chaochao and Chen, Longbiao},
booktitle={Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2023},
pages={673--683},
year={2023}
}

Zheng Wang, Xiaoliang Fan*, Jianzhong Qi, Haibing Jin, Peizhen Yang, Siqi Chen, Cheng Wang
FedGS: Federated Graph-based Sampling with Arbitrary Client Availability
AAAI-23 (CCF A类会议)
 bibtex
bibtex
@inproceedings{wang2023fedgs,
title={Fedgs: Federated graph-based sampling with arbitrary client availability},
author={Wang, Zheng and Fan, Xiaoliang and Qi, Jianzhong and Jin, Haibing and Yang, Peizhen and Shen, Siqi and Wang, Cheng},
booktitle={Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence},
volume={37},
number={8},
pages={10271--10278},
year={2023}
}

Sheng Ao, Qingyong Hu, Hanyun Wang, Kai Xu, Yulan Guo
BUFFER: Balancing Accuracy, Efficiency, and Generalizability in Point Cloud Registration
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)
 bibtex
bibtex
@inproceedings{ao2023buffer,
title={Buffer: Balancing accuracy, efficiency, and generalizability in point cloud registration},
author={Ao, Sheng and Hu, Qingyong and Wang, Hanyun and Xu, Kai and Guo, Yulan},
booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition},
pages={1255--1264},
year={2023}
}

Tieqi Shou, Zhuohan Ye, Yayao Hong, Zhiyuan Wang, Hang Zhu, Zhihan Jiang, Dingqi Yang, Binbin Zhou, Cheng Wang, Longbiao Chen
CrowdQ: Predicting the Queue State of Hospital Emergency Department Using Crowdsensing Mobility Data-Driven Models
UbiComp
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{10.1145/3610875,
author = {Shou, Tieqi and Ye, Zhuohan and Hong, Yayao and Wang, Zhiyuan and Zhu, Hang and Jiang, Zhihan and Yang, Dingqi and Zhou, Binbin and Wang, Cheng and Chen, Longbiao},
title = {CrowdQ: Predicting the Queue State of Hospital Emergency Department Using Crowdsensing Mobility Data-Driven Models},
year = {2023},
issue_date = {September 2023},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
volume = {7},
number = {3},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3610875},
doi = {10.1145/3610875},
abstract = {Hospital Emergency Departments (EDs) are essential for providing emergency medical services, yet often overwhelmed due to increasing healthcare demand. Current methods for monitoring ED queue states, such as manual monitoring, video surveillance, and front-desk registration are inefficient, invasive, and delayed to provide real-time updates. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a novel framework, CrowdQ, which harnesses spatiotemporal crowdsensing data for real-time ED demand sensing, queue state modeling, and prediction. By utilizing vehicle trajectory and urban geographic environment data, CrowdQ can accurately estimate emergency visits from noisy traffic flows. Furthermore, it employs queueing theory to model the complex emergency service process with medical service data, effectively considering spatiotemporal dependencies and event context impact on ED queue states. Experiments conducted on large-scale crowdsensing urban traffic datasets and hospital information system datasets from Xiamen City demonstrate the framework's effectiveness. It achieves an F1 score of 0.93 in ED demand identification, effectively models the ED queue state of key hospitals, and reduces the error in queue state prediction by 18.5\%-71.3\% compared to baseline methods. CrowdQ, therefore, offers valuable alternatives for public emergency treatment information disclosure and maximized medical resource allocation.},
journal = {Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol.},
month = {sep},
articleno = {122},
numpages = {28},
keywords = {Hospital queue state modeling, Mobile trajectory mining, Spatiotemporal crowdsensing data, Urban computing}
}

Yanfei Su , Ming Cheng*, Zhimin Yuan , Weiquan Liu , Wankang Zeng, and Cheng Wang
Multistage Scene-Level Constraints for Large-Scale Point Cloud Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{su2023multi,
title={Multi-stage Scene-level Constraints for Large-scale Point Cloud Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation},
author={Su, Yanfei and Cheng, Ming and Yuan, Zhimin and Liu, Weiquan and Zeng, Wankang and Wang, Cheng},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing},
year={2023},
publisher={IEEE}
}

Yanfei Su, Ming Cheng*, Zhimin Yuan , Weiquan Liu , Wankang Zeng, Zhihong Zhang , and Cheng Wang
Spatial Adaptive Fusion Consistency Contrastive Constraint: Weakly Supervised Building Facade Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{su2023spatial,
title={Spatial adaptive fusion consistency contrastive constraint: weakly supervised building facade point cloud semantic segmentation},
author={Su, Yanfei and Cheng, Ming and Yuan, Zhimin and Liu, Weiquan and Zeng, Wankang and Zhang, Zhihong and Wang, Cheng},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing},
year={2023},
publisher={IEEE}
}

Xiuhong Lin, Changjie Qiu, Zhipeng Cai, Siqi Shen*, Yu Zang, Weiquan Liu, Xuesheng Bian, Matthias Müller, Cheng Wang
E2PNet: Event to Point Cloud Registration with Spatio-Temporal Representation Learning
NeurIPS 2023, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex
{}

Siqi Shen, Chennan Ma, Chao Li, Weiquan Liu, Yongquan Fu*, Songzhu Mei, Xinwang Liu, Cheng Wang
RiskQ: Risk-sensitive Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Value Factorization
NeurIPS 2023, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex
{}

Ruijie Xiao, Chuan Zhong, Wankang Zeng, Ming Cheng*, and Cheng Wang
Novel Convolutions for Semantic Segmentation of Remote Sensing Images
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{xiao2023novel,
title={Novel Convolutions for Semantic Segmentation of Remote Sensing Images},
author={Xiao, Ruijie and Zhong, Chuan and Zeng, Wankang and Cheng, Ming and Wang, Cheng},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing},
year={2023},
publisher={IEEE}
}

Zhimin Yuan, Ming Cheng*, Wankang Zeng, Yanfei Su, Weiquan Liu, Shangshu Yu, and Cheng Wang
Prototype-Guided Multitask Adversarial Network for Cross-Domain LiDAR Point Clouds Semantic Segmentation
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{yuan2023prototype,
title={Prototype-guided Multi-task Adversarial Network for Cross-domain LiDAR Point Clouds Semantic Segmentation},
author={Yuan, Zhimin and Cheng, Ming and Zeng, Wankang and Su, Yanfei and Liu, Weiquan and Yu, Shangshu and Wang, Cheng},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing},
year={2023},
publisher={IEEE}
}

Zhimin Yuan, Chenglu Wen, Ming Cheng*, Yanfei Su, Weiquan Liu, Shangshu Yu, and Cheng Wang
Category-Level Adversaries for Outdoor LiDAR Point Clouds Cross-Domain Semantic Segmentation
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INTELLIGENT TRANSPORTATION SYSTEMS
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{yuan2022category,
title={Category-Level Adversaries for Outdoor LiDAR Point Clouds Cross-Domain Semantic Segmentation},
author={Yuan, Zhimin and Wen, Chenglu and Cheng, Ming and Su, Yanfei and Liu, Weiquan and Yu, Shangshu and Wang, Cheng},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems},
year={2023},
publisher={IEEE}
}

Ming Yan, Xin Wang, Yudi Dai, Siqi Shen*, Chenglu Wen, Lan Xu, Yuexin Ma, Cheng Wang
CIMI4D: A Large Multimodal Climbing Motion Dataset under Human-scene Interactions
CVPR 2023, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex
xx

Wen Li, Shangshu Yu, Cheng Wang, Guosheng Hu, Siqi Shen, Chenglu Wen
SGLoc: Scene Geometry Encoding for Outdoor LiDAR Localization
CVPR 2023, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex
xx

Yongquan Fu, Lun An, Siqi Shen*, Kai Chen, Pere Barlet-Ros
A One-pass Clustering based Sketch Method for Network Monitoring
IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking (ToN), CCF A, 2023
 bibtex
bibtex
xx

Chuanpan Zheng#, Cheng Wang*, Xiaoliang Fan, et al.
STPC-Net: Learn Massive Geo-sensory Data as Spatio-Temporal Point Clouds
IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{zheng2021stpc,
title={STPC-Net: Learn massive geo-sensory data as spatio-temporal point clouds},
author={Zheng, Chuanpan and Wang, Cheng and Fan, Xiaoliang and Qi, Jianzhong and Yan, Xu},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems},
volume={23},
number={8},
pages={11314--11324},
year={2022},
publisher={IEEE}
}

Sheng Ao, Yulan Guo, Qingyong Hu, Bo Yang, Andrew Markham, Zengping Chen
You Only Train Once: Learning General and Distinctive 3D Local Descriptors
IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI)
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{ao2022you,
title={You only train once: Learning general and distinctive 3D local descriptors},
author={Ao, Sheng and Guo, Yulan and Hu, Qingyong and Yang, Bo and Markham, Andrew and Chen, Zengping},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence},
volume={45},
number={3},
pages={3949--3967},
year={2023},
publisher={IEEE}
}

Hang Zhu, Tieqi Shou, Ruiying Guo, Zhihan Jiang, Zeyu Wang, Zhiyuan Wang, Zhiyong Yu, Weijie Zhang, Cheng Wang, Longbiao Chen
RedPacketBike: A graph-based demand modeling and crowd-driven station rebalancing framework for bike sharing systems
TMC
 bibtex
bibtex
@ARTICLE{9693278,
author={Zhu, Hang and Shou, Tieqi and Guo, Ruiying and Jiang, Zhihan and Wang, Zeyu and Wang, Zhiyuan and Yu, Zhiyong and Zhang, Weijie and Wang, Cheng and Chen, Longbiao},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing},
title={RedPacketBike: A Graph-Based Demand Modeling and Crowd-Driven Station Rebalancing Framework for Bike Sharing Systems},
year={2023},
volume={22},
number={7},
pages={4236-4252},
keywords={Task analysis;Market research;Predictive models;Mobile computing;Heuristic algorithms;Deep learning;Spatiotemporal phenomena;Mobile crowdsensing;graph neural networks;bike sharing systems},
doi={10.1109/TMC.2022.3145979}}

Zhihan Jiang, Xin He, Chenhui Lu, Binbin Zhou, Xiaoliang Fan, Cheng Wang, Xiaojuan Ma, Edith C.H. Ngai, Longbiao Chen
Understanding Drivers’ Visual and Comprehension Loads in Traffic Violation Hotspots Leveraging Crowd-Based Driving Simulation
TITS
 bibtex
bibtex
@ARTICLE{9894372,
author={Jiang, Zhihan and He, Xin and Lu, Chenhui and Zhou, Binbin and Fan, Xiaoliang and Wang, Cheng and Ma, Xiaojuan and Ngai, Edith C.H. and Chen, Longbiao},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems},
title={Understanding Drivers’ Visual and Comprehension Loads in Traffic Violation Hotspots Leveraging Crowd-Based Driving Simulation},
year={2022},
volume={23},
number={12},
pages={23369-23383},
keywords={Vehicles;Visualization;Load modeling;Environmental factors;Solid modeling;Three-dimensional displays;Point cloud compression;Traffic violation;crowdsensing;data analytics;driving simulation},
doi={10.1109/TITS.2022.3204068}}

Longbiao Chen, Xin He, Xiantao Zhao, Han Li, Yunyi Huang, Binbin Zhou, Wei Chen, Yongchuan Li, Chenglu Wen, Cheng Wang
GoComfort: Comfortable Navigation for Autonomous Vehicles Leveraging High-Precision Road Damage Crowdsensing
TMC
 bibtex
bibtex
L. Chen et al., "GoComfort: Comfortable Navigation for Autonomous Vehicles Leveraging High-Precision Road Damage Crowdsensing," in IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, vol. 22, no. 11, pp. 6477-6494, 1 Nov. 2023, doi: 10.1109/TMC.2022.3198089.
keywords: {Roads;Sensors;Navigation;Autonomous vehicles;Urban areas;Crowdsensing;Point cloud compression;Comfortable route planning;mobile crowdsensing;road damage identification;urban computing},

Shangbin Wu, Xiaoliang Fan*, Cheng Wang, et al.
Multi-Graph Fusion Networks for Urban Region Embedding
IJCAI-22 (CCF A类会议)
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{wu2022multi,
title={Multi-graph fusion networks for urban region embedding},
author={Wu, Shangbin and Yan, Xu and Fan, Xiaoliang and Pan, Shirui and Zhu, Shichao and Zheng, Chuanpan and Cheng, Ming and Wang, Cheng},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2201.09760},
year={2022}
}

Siqi Shen, Mengwei Qiu, Jun Liu, Weiquan Liu, Yongquan Fu*, Xinwang Liu, Cheng Wang
ResQ: A Residual Q Function-based Approach for Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Value Factorization
NeurIPS 2022, Spotlight, CCF A, top 5%
 bibtex
bibtex
@inproceedings{ResQ,
author = {Siqi Shen and
Mengwei Qiu and
Jun Liu and
Weiquan Liu and Yongquan Fu and Xinwang Liu and Cheng Wang},
title = {ResQ: A Residual Q Function-based Approach for Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Value Factorization},
booktitle = {{NeurIPS}},
year = {2022}
}

Weiquan Liu, Hanyun Guo, Weini Zhang, Yu Zang*, Cheng Wang, Jonathan Li
TopoSeg: Topology-aware Segmentation for Point Clouds
International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence Organization (IJCAI)
 bibtex
bibtex
@inproceedings{ijcai2022-168,
title = {TopoSeg: Topology-aware Segmentation for Point Clouds},
author = {Liu, Weiquan and Guo, Hanyun and Zhang, Weini and Zang, Yu and Wang, Cheng and Li, Jonathan},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Thirty-First International Joint Conference on
Artificial Intelligence, {IJCAI-22}},
publisher = {International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence Organization},
editor = {Lud De Raedt},
pages = {1201--1208},
year = {2022},
month = {7},
note = {Main Track}
doi = {10.24963/ijcai.2022/168},
url = {https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2022/168},
}

Xiaoliang Fan, Yakun Hu, Zibin Zheng*, et al.
CASR-TSE: Context-Aware Web Services Recommendation for Modeling Weighted Temporal-Spatial Effectiveness
IEEE Transactions on Services Computing (CCF A类期刊)
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{fan2017casr,
title={CASR-TSE: Context-aware web services recommendation for modeling weighted temporal-spatial effectiveness},
author={Fan, Xiaoliang and Hu, Yakun and Zheng, Zibin and Wang, Yujie and Br{\'e}zillon, Patrick and Chen, Wenbo},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Services Computing},
volume={14},
number={1},
pages={58--70},
year={2021},
publisher={IEEE}
}

Zheng Wang, Xiaoliang Fan*, Jianzhong Qi, Cheng Wang, et al.
Federated Learning with Fair Averaging
IJCAI-21 (CCF A类会议)
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{wang2021federated,
title={Federated learning with fair averaging},
author={Wang, Zheng and Fan, Xiaoliang and Qi, Jianzhong and Wen, Chenglu and Wang, Cheng and Yu, Rongshan},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.14937},
year={2021}
}

Sheng Ao, Qingyong Hu, Bo Yang, Andrew Markham, Yulan Guo
SpinNet: Learning a General Surface Descriptor for 3D Point Cloud Registration
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)
 bibtex
bibtex
@inproceedings{ao2021spinnet,
title={Spinnet: Learning a general surface descriptor for 3d point cloud registration},
author={Ao, Sheng and Hu, Qingyong and Yang, Bo and Markham, Andrew and Guo, Yulan},
booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition},
pages={11753--11762},
year={2021}
}

Zhihan Jiang, Hang Zhu, Binbin Zhou, Chenhui Lu, Mingfei Sun, Xiaojuan Ma, Xiaoliang Fan, Cheng Wang, Longbiao Chen
CrowdPatrol: A mobile crowdsensing framework for traffic violation hotspot patrolling
TMC
 bibtex
bibtex
@ARTICLE{9531409,
author={Jiang, Zhihan and Zhu, Hang and Zhou, Binbin and Lu, Chenhui and Sun, Mingfei and Ma, Xiaojuan and Fan, Xiaoliang and Wang, Cheng and Chen, Longbiao},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing},
title={CrowdPatrol: A Mobile Crowdsensing Framework for Traffic Violation Hotspot Patrolling},
year={2023},
volume={22},
number={3},
pages={1401-1416},
keywords={Roads;Crowdsensing;Urban areas;Task analysis;Schedules;Law enforcement;Context modeling;Traffic violation;urban computing;patrol task scheduling;mobile crowdsensing},
doi={10.1109/TMC.2021.3110592}}

Longbiao Chen, Chenhui Lu, Fangxu Yuan, Zhihan Jiang, Leye Wang, Daqing Zhang, Ruixiang Luo, Xiaoliang Fan, Cheng Wang
UVLens: urban village boundary identification and population estimation leveraging open government data
UbiComp
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{10.1145/3463495,
author = {Chen, Longbiao and Lu, Chenhui and Yuan, Fangxu and Jiang, Zhihan and Wang, Leye and Zhang, Daqing and Luo, Ruixiang and Fan, Xiaoliang and Wang, Cheng},
title = {UVLens: Urban Village Boundary Identification and Population Estimation Leveraging Open Government Data},
year = {2021},
issue_date = {June 2021},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
volume = {5},
number = {2},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3463495},
doi = {10.1145/3463495},
abstract = {Urban villages refer to the residential areas lagging behind the rapid urbanization process in many developing countries. These areas are usually with overcrowded buildings, high population density, and low living standards, bringing potential risks of public safety and hindering the urban development. Therefore, it is crucial for urban authorities to identify the boundaries of urban villages and estimate their resident and floating populations so as to better renovate and manage these areas. Traditional approaches, such as field surveys and demographic census, are time consuming and labor intensive, lacking a comprehensive understanding of urban villages. Against this background, we propose a two-phase framework for urban village boundary identification and population estimation. Specifically, based on heterogeneous open government data, the proposed framework can not only accurately identify the boundaries of urban villages from large-scale satellite imagery by fusing road networks guided patches with bike-sharing drop-off patterns, but also accurately estimate the resident and floating populations of urban villages with a proposed multi-view neural network model. We evaluate our method leveraging real-world datasets collected from Xiamen Island. Results show that our framework can accurately identify the urban village boundaries with an IoU of 0.827, and estimate the resident population and floating population with R2 of 0.92 and 0.94 respectively, outperforming the baseline methods. We also deploy our system on the Xiamen Open Government Data Platform to provide services to both urban authorities and citizens.},
journal = {Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol.},
month = {jun},
articleno = {57},
numpages = {26},
keywords = {urban village, urban computing, population estimation, heterogeneous data}
}

Linwei Chen, Bowen Fang, Lei Zhao, Yu Zang* , et al.
DeepUrbanDownscale: A physics informed deep learning framework for high-resolution urban surface temperature estimation via 3D point clouds
International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{0DeepUrbanDownscale,
title={DeepUrbanDownscale: A physics informed deep learning framework for high-resolution urban surface temperature estimation via 3D point clouds - ScienceDirect},
author={ Lc, A and Bf, C and Lei, Z. C. and Yu, Z. A. and Wl, A and Yc, A and Cheng, W. A. and Jla, B },
journal={International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation},
volume={106},
}

Yongquan Fu, Lun An, Kai Chen, Pere Barlet-Ros, Siqi Shen*
Jellyfish: Locality-sensitive Subflow Sketching
INFOCOM, 2021, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{Fu2021JellyfishLS,
title={Jellyfish: Locality-Sensitive Subflow Sketching},
author={Yongquan Fu and Lun An and Siqi Shen and Kai Chen and Pere Barlet-Ros},
journal={IEEE INFOCOM 2021 - IEEE Conference on Computer Communications},
year={2021},
pages={1-10}
}

Siqi Shen, Yongquan Fu*, Huayou Su, Hengyue Pan, Peng Qiao, Yong Dou, Cheng Wang*
GRAPHCOMM: A GRAPH NEURAL NETWORK BASED METHOD FOR MULTI-AGENT REINFORCEMENT LEARNING
ICASSP 2021, CCF B
 bibtex
bibtex
@inproceedings{GraphComm,
author = {Siqi Shen and
Yongquan Fu and
Huayou Su and
Hengyue Pan and
Peng Qiao and
Yong Dou and
Cheng Wang},
title = {Graphcomm: {A} Graph Neural Network Based Method for Multi-Agent Reinforcement
Learning},
booktitle = {{ICASSP}},
pages = {3510--3514},
year = {2021},
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, https://dblp.org}
}

Chenglu Wen, Jinbin Tan, Fashuai Li, Chongrong Wu, Yitai Lin, Zhiyong Wang, Cheng Wang
Cooperative indoor 3D mapping and modeling using LiDAR data
Information Sciences
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{WEN2021192,
title = {Cooperative indoor 3D mapping and modeling using LiDAR data},
journal = {Information Sciences},
volume = {574},
pages = {192-209},
year = {2021},
issn = {0020-0255},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2021.06.006},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0020025521005934},
author = {Chenglu Wen and Jinbin Tan and Fashuai Li and Chongrong Wu and Yitai Lin and Zhiyong Wang and Cheng Wang},
keywords = {Frame-level semantic labeling, Line model, Point-cloud-based mapping},
abstract = {Point clouds and models with semantic information facilitate various indoor automation, ranging from indoor robotics to emergency responses. Studies are currently being conducted on semantic labeling and modeling based on offline mapped point clouds, in which, the performance is strongly limited by the mapping process. To address this issue, we propose a framework to cooperatively perform the three tasks of semantic labeling, mapping, and 3D modeling of point clouds. First, our framework uses a deep-learning-assisted method to perform frame-level point cloud semantic labeling. Subsequently, point cloud frames with semantic labels are used to extract the structural planes of buildings, followed by the generation of line structures from the planes. Then, these frames are used to estimate the initial poses of a 3D sensor for data collection. In the subsequent pose optimization process, the initial poses are optimized under the constraints of the structural planes. Finally, the optimized poses are used to integrate semantic frames and line structures to generate a point cloud map and 3D line model of buildings. The experimental results show that the proposed method achieves better results than the state-of-the-art methods that separately perform one of the two tasks.}
}

Yudi Dai, Chenglu Wen*, Hai Wu, Yulan Guo, Longbiao Chen, Cheng Wang
Indoor 3D Human Trajectory Reconstruction Using Surveillance Camera Videos and Point Clouds
IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology
 bibtex
bibtex
@ARTICLE{9433501, author={Dai, Yudi and Wen, Chenglu and Wu, Hai and Guo, Yulan and Chen, Longbiao and Wang, Cheng}, journal={IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology}, title={Indoor 3D Human Trajectory Reconstruction Using Surveillance Camera Videos and Point Clouds}, year={2021}, volume={}, number={}, pages={1-1}, doi={10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3081591}}

Hai Wu, Wenkai Han, Chenglu Wen*, Xin Li, Cheng Wang
3D Multi-Object Tracking in Point Clouds Based on Prediction Confidence-Guided Data Association
IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems
 bibtex
bibtex
@ARTICLE{9352500, author={Wu, Hai and Han, Wenkai and Wen, Chenglu and Li, Xin and Wang, Cheng}, journal={IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems}, title={3D Multi-Object Tracking in Point Clouds Based on Prediction Confidence-Guided Data Association}, year={2021}, volume={}, number={}, pages={1-10}, doi={10.1109/TITS.2021.3055616}}

W Liu, B Lai, C Wang*, X Bian, C Wen, M Cheng, Y Zang, Y Xia, J Li
Matching 2D Image Patches and 3D Point Cloud Volumes by Learning Local Cross-domain Feature Descriptors
2021 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces Abstracts and Workshops (VRW)
 bibtex
bibtex
@inproceedings{liu2021matching,
title={Matching 2D Image Patches and 3D Point Cloud Volumes by Learning Local Cross-domain Feature Descriptors},
author={Liu, Weiquan and Lai, Baiqi and Wang, Cheng and Bian, Xuesheng and Wen, Chenglu and Cheng, Ming and Zang, Yu and Xia, Yan and Li, Jonathan},
booktitle={2021 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces Abstracts and Workshops (VRW)},
pages={516--517},
year={2021},
organization={IEEE}
}

Yongquan Fu, Lun An, Kai Chen, Pere Barlet-Ros, Siqi Shen
Jellyfish: Locality-sensitive Subflow Sketching
INFOCOM 2021, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex
312312
321312

Longbiao Chen, Thi-Mai-Trang Nguyen, Dingqi Yang, Michele Nogueira, Cheng Wang, Daqing Zhang
Data-driven C-RAN optimization exploiting traffic and mobility dynamics of mobile users
TMC
 bibtex
bibtex
@ARTICLE{8981890,
author={Chen, Longbiao and Nguyen, Thi-Mai-Trang and Yang, Dingqi and Nogueira, Michele and Wang, Cheng and Zhang, Daqing},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing},
title={Data-Driven C-RAN Optimization Exploiting Traffic and Mobility Dynamics of Mobile Users},
year={2021},
volume={20},
number={5},
pages={1773-1788},
keywords={Handover;Optimization;Cellular networks;Computer architecture;Mobile computing;Base stations;Cellular network;C-RAN optimization;deep learning;big data analytics},
doi={10.1109/TMC.2020.2971470}}

Chuanpan Zheng, Xiaoliang Fan*, Cheng Wang, et al.
GMAN: A Graph Multi-Attention Network for Traffic Prediction
AAAI-20 (CCF A类会议)
 bibtex
bibtex
@inproceedings{zheng2020gman,
title={Gman: A graph multi-attention network for traffic prediction},
author={Zheng, Chuanpan and Fan, Xiaoliang and Wang, Cheng and Qi, Jianzhong},
booktitle={Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence},
volume={34},
number={01},
pages={1234--1241},
year={2020}
}

Y. Zhang, K. Huo, Z. Liu, Y. Zang*, C. Wang et al
PGNet: A Part-based Generative Network for 3D Object Reconstruction
Knowledge based System
 bibtex
bibtex
null

W. Zhang, L. Chen, Z. Xiong, Y. Zang* et al.
Large-scale point cloud contour extraction via 3D guided multi-conditional generative adversarial network
ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing
 bibtex
bibtex
null

Adele Lu Jia, Yuanxing Rao, Hongru Li, Ran Tian, Siqi Shen*
Revealing Donation Dynamics in Social Live Video Streaming
WWW 2020, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex
@inbook{10.1145/3366424.3382682,
author = {Lu Jia, Adele and Rao, Yuanxing and Li, Hongru and Tian, Ran and Shen, Siqi},
title = {Revealing Donation Dynamics in Social Live Video Streaming},
year = {2020},
isbn = {9781450370240},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3366424.3382682},
abstract = {Social live video streaming has become a global economic and social phenomenon with the rise of platforms like Facebook-Live, Youtube-Live, and Twitch. The phenomenon of user donation in these communities is rapidly emerging, towards which however we have very limited understandings. In this preliminary work, we reveal the dynamics of user donations based on a publicly available (anonymized) dataset with detailed information on over 2 million users and worth in total over 200 million US dollars. Among other results, we find that (i) both the donations received and the donations made are highly skewed, (ii) user donation is strongly correlated with the atmosphere (the volume and the sentiment of real-time user chats) and in the long run, the loss of broadcasters, and (iii) donors are loyal and very generous to their favorite broadcasters while in the mean time they also support others moderately. Our findings represent a first step towards understanding user donations which will shed lights on the donor retention problem and the design of social live video streaming services. },
booktitle = {Companion Proceedings of the Web Conference 2020},
pages = {30–31},
numpages = {2}
}

Siqi Shen*, Yongquan Fu, Adele Lu Jia, Huayou Su, Qinglin Wang, Chengsong Wang, Yong Dou
Learning Network Representation Through Reinforcement Learning
ICASSP 2020, CCF B
 bibtex
bibtex
@INPROCEEDINGS{9053879,
author={Shen, Siqi and Fu, Yongquan and Jia, Adele Lu and Su, Huayou and Wang, Qinglin and Wang, Chengsong and Dou, Yong},
booktitle={ICASSP 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP)},
title={Learning Network Representation Through Reinforcement Learning},
year={2020},
volume={},
number={},
pages={3537-3541},
doi={10.1109/ICASSP40776.2020.9053879}}

Yongquan Fu, Dongsheng Li, Siqi Shen*, Yiming Zhang, Kai Chen
Clustering-preserving Network Flow Sketching
INFOCOM 2020, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex
@INPROCEEDINGS{9155388,
author={Fu, Yongquan and Li, Dongsheng and Shen, Siqi and Zhang, Yiming and Chen, Kai},
booktitle={IEEE INFOCOM 2020 - IEEE Conference on Computer Communications},
title={Clustering-preserving Network Flow Sketching},
year={2020},
volume={},
number={},
pages={1309-1318},
doi={10.1109/INFOCOM41043.2020.9155388}}

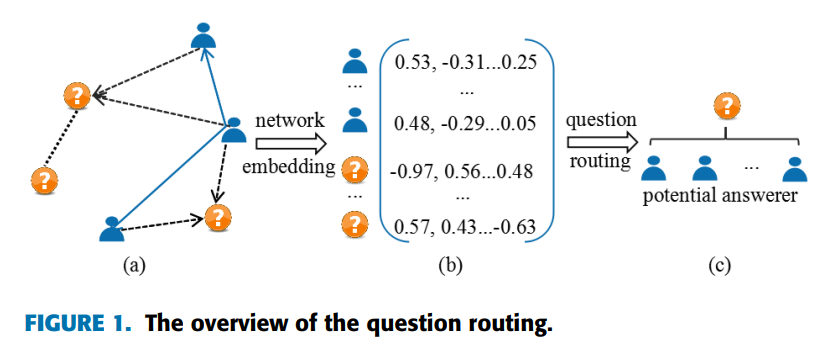
Xiaoxue Shen, Adele Lu Jia, Siqi Shen*, Yong Dou, Helping the ineloquent farmers: Finding experts for questions with limited text in agricultural Q&A Communities
Helping the ineloquent farmers: Finding experts for questions with limited text in agricultural Q&A Communities
IEEE ACCESS 2020, JCR 2
 bibtex
bibtex
@ARTICLE{9050735,
author={Shen, Xiaoxue and Jia, Adele Lu and Shen, Siqi and Dou, Yong},
journal={IEEE Access},
title={Helping the Ineloquent Farmers: Finding Experts for Questions With Limited Text in Agricultural Q amp;A Communities},
year={2020},
volume={8},
number={},
pages={62238-62247},
doi={10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2984342}}

W. Zhang, L. Chen, Z. Xiong, Y. Zang et al.
Large-scale point cloud contour extraction via 3D guided multi-conditional generative adversarial network
ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{zhang2020large,
title={Large-scale point cloud contour extraction via 3D guided multi-conditional generative adversarial network},
author={Zhang, Weini and Chen, Linwei and Xiong, Zhangyue and Zang, Yu and Li, Jonathan and Zhao, Lei},
journal={ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing},
volume={164},
pages={97--105},
year={2020},
publisher={Elsevier}
}

Y. Zhang, K. Huo, Z. Liu, Y. Zang, C. Wang et al.
PGNet: A Part-based Generative Network for 3D Object Reconstruction
Knowledge based System
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{zhang2020pgnet,
title={PGNet: A Part-based Generative Network for 3D object reconstruction},
author={Zhang, Yang and Huo, Kai and Liu, Zhen and Zang, Yu and Liu, Yongxiang and Li, Xiang and Zhang, Qianyu and Wang, Cheng},
journal={Knowledge-Based Systems},
volume={194},
pages={105574},
year={2020},
publisher={Elsevier}
}

Cheng Wang, Yudi Dai, Naser Elsheimy, Chenglu Wen, Guenther Retscher, Zhizhong Kang, Andrea Lingua
ISPRS BENCHMARK ON MULTISENSORY INDOOR MAPPING AND POSITIONING.
ISPRS Annals of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing & Spatial Information Sciences
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{wang2020isprs,
title={ISPRS BENCHMARK ON MULTISENSORY INDOOR MAPPING AND POSITIONING.},
author={Wang, Cheng and Dai, Yudi and Elsheimy, Naser and Wen, Chenglu and Retscher, Guenther and Kang, Zhizhong and Lingua, Andrea},
journal={ISPRS Annals of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing \& Spatial Information Sciences},
volume={5},
number={5},
year={2020}
}

Wenkai Han, Chenglu Wen*, Cheng Wang, Xin Li, Qing Li
Point2Node: Correlation learning of dynamic-node for point cloud feature modeling
AAAI
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{Han_Wen_Wang_Li_Li_2020, title={Point2Node: Correlation Learning of Dynamic-Node for Point Cloud Feature Modeling}, volume={34}, url={https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/view/6725}, DOI={10.1609/aaai.v34i07.6725}, abstractNote={<p>Fully exploring correlation among points in point clouds is essential for their feature modeling. This paper presents a novel end-to-end graph model, named Point2Node, to represent a given point cloud. Point2Node can dynamically explore correlation among all graph nodes from different levels, and adaptively aggregate the learned features. Specifically, first, to fully explore the spatial correlation among points for enhanced feature description, in a high-dimensional node graph, we dynamically integrate the node’s correlation with self, local, and non-local nodes. Second, to more effectively integrate learned features, we design a data-aware gate mechanism to self-adaptively aggregate features at the channel level. Extensive experiments on various point cloud benchmarks demonstrate that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art.</p>}, number={07}, journal={Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence}, author={Han, Wenkai and Wen, Chenglu and Wang, Cheng and Li, Xin and Li, Qing}, year={2020}, month={Apr.}, pages={10925-10932} }

S Wang, G Cai*, M Cheng, JM Junior, S Huang, Z Wang, S Su, J Li
Robust 3D reconstruction of building surfaces from point clouds based on structural and closed constraints
ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{wang2020robust,
title={Robust 3D reconstruction of building surfaces from point clouds based on structural and closed constraints},
author={Wang, Senyuan and Cai, Guorong and Cheng, Ming and Junior, Jos{\'e} Marcato and Huang, Shangfeng and Wang, Zongyue and Su, Songzhi and Li, Jonathan},
journal={ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing},
volume={170},
pages={29--44},
year={2020},
publisher={Elsevier}
}

Yongquan Fu, Dongsheng Li, Siqi Shen, Yiming Zhang, Kai Chen
Clustering-preserving Network Flow Sketching
2020, INFOCOM, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex
312312
321312

Siqi Shen, Yongquan Fu, Adele Lu Jia, Huayou Su, Qinglin Wang, Chengsong Wang, Yong Dou
Learning Network Representation Through Reinforcement Learning
ICASSP, 2020, CCF B
 bibtex
bibtex
312312
321312

Adele Lu Jia, Yuanxing Rao, Hongru Li, Ran Tian, Siqi Shen
Revealing Donation Dynamics in Social Live Video Streaming
WWW 2020, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex
312312
321312

Shanxin Zhang, Cheng Wang, Zijian He, Qing Li, Xiuhong Lin, Xin Li, Juyong Zhang,Chenhui Yang, Jonathan Li
Vehicle global 6-DoF pose estimation under traffic surveillance camera
ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing
 bibtex
bibtex
312312
321312

Zhipeng Luo, Di Liu, Jonathan Li, Yiping Chen, Zhenlong Xiao, José Marcato Junior,Wesley Nunes Gonçalves, Cheng Wang
Learning sequential slice representation with an attention-embedding network for 3D shape recognition and retrieval in MLS point clouds
ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing
 bibtex
bibtex
312312
321312

Zheng Gonga,, Haojia Lin, Dedong Zhang, Zhipeng Luo, John Zelek, Yiping Chen,Abdul Nurunnabi, Cheng Wang, Jonathan Li
A Frustum-based probabilistic framework for 3D object detection by fusion of LiDAR and camera data
ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing
 bibtex
bibtex
312312
321312

Yangbin Lin, Jialian Li, Cheng Wang, Zhonggui Chen, Zongyue Wang, Jonathan Li
Fast regularity-constrained plane fitting
ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing
 bibtex
bibtex
312312
321312

Chuanpan Zheng; Xiaoliang Fan*, Cheng Wang et al.
DeepSTD: Mining Spatio-temporal Disturbances of Multiple Context Factors for Citywide Traffic Flow Prediction
IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{zheng2019deepstd,
title={DeepSTD: Mining spatio-temporal disturbances of multiple context factors for citywide traffic flow prediction},
author={Zheng, Chuanpan and Fan, Xiaoliang and Wen, Chenglu and Chen, Longbiao and Wang, Cheng and Li, Jonathan},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems},
volume={21},
number={9},
pages={3744--3755},
year={2019},
publisher={IEEE}
}

Y. Zhang, Z. Xiong, Y. Zang*, et al.
Topology-aware road network extraction via multi-supervised generative adversarial networks
Remote Sensing
 bibtex
bibtex
null

Liwen Peng, Siqi Shen*, Jun Xu, Yongquan Fu, Dongsheng Li, Adele lu Jia. Diting: An Author Disambiguation method based on Network Representation Learning
Diting: An Author Disambiguation method based on Network Representation Learning
IEEE ACCESS 2019, JCR 2
 bibtex
bibtex
@ARTICLE{8844683,
author={Peng, Liwen and Shen, Siqi and Xu, Jun and Fu, Yongquan and Li, Dongsheng and Jia, Adele Lu},
journal={IEEE Access},
title={Diting: An Author Disambiguation Method Based on Network Representation Learning},
year={2019},
volume={7},
number={},
pages={135539-135555},
doi={10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2942477}}

Yongquan Fu, Dongsheng Li, Pere Barlet-Ros, Chun Huang, Zhen Huang, Siqi Shen, Huayou Su
A Skewness-aware Matrix Factorization Approach for Mesh-structured Cloud Services
IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking 2019, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{10.1109/TNET.2019.2923815,
author = {Fu, Yongquan and Li, Dongsheng and Barlet-Ros, Pere and Huang, Chun and Huang, Zhen and Shen, Siqi and Su, Huayou},
title = {A Skewness-Aware Matrix Factorization Approach for Mesh-Structured Cloud Services},
year = {2019},
issue_date = {August 2019},
publisher = {IEEE Press},
volume = {27},
number = {4},
issn = {1063-6692},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1109/TNET.2019.2923815},
doi = {10.1109/TNET.2019.2923815},
abstract = {Online cloud services need to fulfill clients’ requests scalably and fast. State-of-the-art cloud services are increasingly deployed as a distributed service mesh. Service to service communication is frequent in the mesh. Unfortunately, problematic events may occur between any pair of nodes in the mesh, therefore, it is vital to maximize the network visibility. A state-of-the-art approach is to model pairwise RTTs based on a latent factor model represented as a low-rank matrix factorization. A latent factor corresponds to a rank-1 component in the factorization model, and is shared by all node pairs. However, different node pairs usually experience a skewed set of hidden factors, which should be fully considered in the model. In this paper, we propose a skewness-aware matrix factorization method named SMF. We decompose the matrix factorization into basic units of rank-one latent factors, and progressively combine rank-one factors for different node pairs. We present a unifying framework to automatically and adaptively select the rank-one factors for each node pair, which not only preserves the low rankness of the matrix model, but also adapts to skewed network latency distributions. Over real-world RTT data sets, SMF significantly improves the relative error by a factor of 0.2 $times$ to 10 $times$ , converges fast and stably, and compactly captures fine-grained local and global network latency structures.},
journal = {IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw.},
month = {aug},
pages = {1598–1611},
numpages = {14}
}

Liwen Peng, Siqi Shen*, Dongsheng Li, Jun Xu, Yongquan Fu, Huayou Su
Author Disambiguation through Adversarial Network Representation Learning
IJCNN 2019, CCF C
 bibtex
bibtex

Y. Zhang, Z. Xiong, Y. Zang, et al.
Topology-aware road network extraction via multi-supervised generative adversarial networks
Remote Sensing
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{zhang2019topology,
title={Topology-aware road network extraction via multi-supervised generative adversarial networks},
author={Zhang, Yang and Xiong, Zhangyue and Zang, Yu and Wang, Cheng and Li, Jonathan and Li, Xiang},
journal={Remote Sensing},
volume={11},
number={9},
pages={1017},
year={2019},
publisher={Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute}
}

Zongliang Zhang, Chenglu Wen, Yiping Chen, Wei Li, Changbin You, Chao Wang, J Li
Indoor scene registration based on siamese network and pointnet
ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{zhang2019indoor,
title={Indoor scene registration based on siamese network and pointnet},
author={Zhang, Zongliang and Wen, Chenglu and Chen, Yiping and Li, Wei and You, Changbin and Wang, Chao and Li, J},
journal={ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences},
volume={4},
pages={307--312},
year={2019},
publisher={Copernicus GmbH}
}

Cheng Wang, Yudi Dai, Naser El-Sheimy, Chenglu Wen, Guenther Retscher, Zhizhong Kang, Andrea Lingua
PROGRESS ON ISPRS BENCHMARK ON MULTISENSORY INDOOR MAPPING AND POSITIONING.
International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing & Spatial Information Sciences
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{wang2019progress,
title={PROGRESS ON ISPRS BENCHMARK ON MULTISENSORY INDOOR MAPPING AND POSITIONING.},
author={Wang, Cheng and Dai, Yudi and El-Sheimy, Naser and Wen, Chenglu and Retscher, Guenther and Kang, Zhizhong and Lingua, Andrea},
journal={International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing \& Spatial Information Sciences},
year={2019}
}

Chenglu Wen, Changbin You, Hai Wu, Cheng Wang, Xiaoliang Fan, Jonathan Li
Recovery of urban 3D road boundary via multi-source data
ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{WEN2019184,
title = {Recovery of urban 3D road boundary via multi-source data},
journal = {ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing},
volume = {156},
pages = {184-201},
year = {2019},
issn = {0924-2716},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2019.08.010},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0924271619301947},
author = {Chenglu Wen and Changbin You and Hai Wu and Cheng Wang and Xiaoliang Fan and Jonathan Li},
keywords = {Point clouds, Mobile laser scanning, 3D road boundary, Multi-source data, GPS trajectory data, Remote sensing image},
abstract = {The mapping of road boundaries provides critical information about roads for urban road traffic safety. This paper presents a deep learning-based framework for recovering 3D road boundary using multi-source data, which include mobile laser scanning (MLS) point clouds, spatial trajectory data, and remote sensing images. The proposed road recovery method uses extracted 3D road boundaries from MLS point clouds as inputs. First, after automatic erroneous boundary removal, a CNN-based boundary completion model completes road boundaries. Then, to refine the imperfect road boundaries, road centerlines generated from dynamic taxi GPS trajectory data and remote sensing images are used as completion guidance for a generative adversarial nets model to obtain more accurate and complete road boundaries. Finally, after associating a sequence of taxi GPS recorded trajectory points with the correct 3D road boundaries, inherent geometric road characteristics and road dynamic information are extracted from the complete boundaries and taxi GPS trajectory data, respectively. The testing dataset contains two urban road MLS datasets, and the KITTI dataset. The experimental results on point clouds from different sensors demonstrate our proposed method is effective and promising for recovering 3D road boundary and extracting road characteristics.}
}

Q Fan, F Chen*, M Cheng, S Lou, R Xiao, B Zhang, C Wang, J Li
Ship detection using a fully convolutional network with compact polarimetric SAR images
Remote Sensing
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{fan2019ship,
title={Ship detection using a fully convolutional network with compact polarimetric SAR images},
author={Fan, Qiancong and Chen, Feng and Cheng, Ming and Lou, Shenlong and Xiao, Rulin and Zhang, Biao and Wang, Cheng and Li, Jonathan},
journal={Remote Sensing},
volume={11},
number={18},
pages={2171},
year={2019},
publisher={Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute}
}

C Wang, M Cheng*, F Sohel, M Bennamoun, J Li
NormalNet: A voxel-based CNN for 3D object classification and retrieval
Neurocomputing
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{wang2019normalnet,
title={NormalNet: A voxel-based CNN for 3D object classification and retrieval},
author={Wang, Cheng and Cheng, Ming and Sohel, Ferdous and Bennamoun, Mohammed and Li, Jonathan},
journal={Neurocomputing},
volume={323},
pages={139--147},
year={2019},
publisher={Elsevier}
}

Li, Q., Chen, S., Wang, C., Li, X., Wen, C., Cheng, M., Li, J.
Lo-net: Deep real-time lidar odometry
CVPR 2019
 bibtex
bibtex
@inproceedings{DBLP:conf/cvpr/LiC0LW0L19,
author = {Qing Li and
Shaoyang Chen and
Cheng Wang and
Xin Li and
Chenglu Wen and
Ming Cheng and
Jonathan Li},
title = {LO-Net: Deep Real-Time Lidar Odometry},
booktitle = {{IEEE} Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, {CVPR}
2019, Long Beach, CA, USA, June 16-20, 2019},
pages = {8473--8482},
publisher = {Computer Vision Foundation / {IEEE}},
year = {2019},
url = {http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content\_CVPR\_2019/html/Li\_LO-Net\_Deep\_Real-Time\_Lidar\_Odometry\_CVPR\_2019\_paper.html},
doi = {10.1109/CVPR.2019.00867},
timestamp = {Mon, 30 Aug 2021 17:01:14 +0200},
biburl = {https://dblp.org/rec/conf/cvpr/LiC0LW0L19.bib},
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, https://dblp.org}
}

Shen, X., Wang, C., Li, X., Yu, Z., Li, J., Wen, C., Cheng, M., He, Z
RF-net: An end-to-end image matching network based on receptive field
CVPR 2019
 bibtex
bibtex
@inproceedings{DBLP:conf/cvpr/Shen0LYLW0H19,
author = {Xuelun Shen and
Cheng Wang and
Xin Li and
Zenglei Yu and
Jonathan Li and
Chenglu Wen and
Ming Cheng and
Zijian He},
title = {RF-Net: An End-To-End Image Matching Network Based on Receptive Field},
booktitle = {{IEEE} Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, {CVPR}
2019, Long Beach, CA, USA, June 16-20, 2019},
pages = {8132--8140},
publisher = {Computer Vision Foundation / {IEEE}},
year = {2019},
url = {http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content\_CVPR\_2019/html/Shen\_RF-Net\_An\_End-To-End\_Image\_Matching\_Network\_Based\_on\_Receptive\_Field\_CVPR\_2019\_paper.html},
doi = {10.1109/CVPR.2019.00832},
timestamp = {Mon, 30 Aug 2021 17:01:14 +0200},
biburl = {https://dblp.org/rec/conf/cvpr/Shen0LYLW0H19.bib},
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, https://dblp.org}
}

Liu, W., Wang, C., Zang, Y., Lai, S.-H., Weng, D., Sian, X., Lin, X., Shen, X., Li, J.
Ground camera images and UAV 3D model registration for outdoor augmented reality
IEEE VR 2019
 bibtex
bibtex
@inproceedings{DBLP:conf/vr/LiuWZLWSLSL19,
author = {Weiquan Liu and
Cheng Wang and
Yu Zang and
Shang{-}Hong Lai and
Dongdong Weng and
Xuesheng Sian and
Xiuhong Lin and
Xuelun Shen and
Jonathan Li},
title = {Ground Camera Images and {UAV} 3D Model Registration for Outdoor Augmented
Reality},
booktitle = {{IEEE} Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces, {VR}
2019, Osaka, Japan, March 23-27, 2019},
pages = {1050--1051},
publisher = {{IEEE}},
year = {2019},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1109/VR.2019.8797821},
doi = {10.1109/VR.2019.8797821},
timestamp = {Fri, 09 Apr 2021 18:51:40 +0200},
biburl = {https://dblp.org/rec/conf/vr/LiuWZLWSLSL19.bib},
bibsource = {dblp computer science bibliography, https://dblp.org}
}

Yongquan Fu, Dongsheng Li, Pere Barlet-Ros, Chun Huang, Zhen Huang, Siqi Shen, Huayou Su
A Skewness-aware Matrix Factorization Approach for Mesh-structured Cloud Services
IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2019, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex
312312
321312

Yongquan Fu, Dongsheng Li, Siqi Shen, Yiming Zhang, Kai Chen
Resilient Disaggregated Network Flow Monitoring
SIGCOMM, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex
312312
321312

Longbiao Chen, Xiaoliang Fan, Leye Wang, Daqing Zhang, Zhiyong Yu, Jonathan Li, Thi-Mai-Trang Nguyen, Gang Pan, Cheng Wang
RADAR: road obstacle identification for disaster response leveraging cross-domain urban data
UbiComp
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{10.1145/3161159,
author = {Chen, Longbiao and Fan, Xiaoliang and Wang, Leye and Zhang, Daqing and Yu, Zhiyong and Li, Jonathan and Nguyen, Thi-Mai-Trang and Pan, Gang and Wang, Cheng},
title = {RADAR: Road Obstacle Identification for Disaster Response Leveraging Cross-Domain Urban Data},
year = {2018},
issue_date = {December 2017},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
volume = {1},
number = {4},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3161159},
doi = {10.1145/3161159},
abstract = {Typhoons and hurricanes cause extensive damage to coast cities annually, demanding urban authorities to take effective actions in disaster response to reduce losses. One of the first priority in disaster response is to identify and clear road obstacles, such as fallen trees and ponding water, and restore road transportation in a timely manner for supply and rescue. Traditionally, identifying road obstacles is done by manual investigation and reporting, which is labor intensive and time consuming, hindering the timely restoration of transportation. In this work, we propose RADAR, a low-cost and real-time approach to identify road obstacles leveraging large-scale vehicle trajectory data and heterogeneous road environment sensing data. First, based on the observation that road obstacles may cause abnormal slow motion behaviors of vehicles in the surrounding road segments, we propose a cluster direct robust matrix factorization (CDRMF) approach to detect road obstacles by identifying the collective anomalies of slow motion behaviors from vehicle trajectory data. Then, we classify the detected road obstacles leveraging the correlated spatial and temporal features extracted from various road environment data, including satellite images and meteorological records. To address the challenges of heterogeneous features and sparse labels, we propose a semi-supervised approach combining co-training and active learning (CORAL). Real experiments on Xiamen City show that our approach accurately detects and classifies the road obstacles during the 2016 typhoon season with precision and recall both above 90\%, and outperforms the state-of-the-art baselines.},
journal = {Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol.},
month = {jan},
articleno = {130},
numpages = {23},
keywords = {urban computing, disaster response, cross-domain data, Mobility data mining}
}

Jun Xu, Siqi Shen*, Dongsheng Li, Yongquan Fu
A Network-embedding Based Method for Author Disambiguation
CIKM 2018, CCF B
 bibtex
bibtex

Adele Lu Jia, Siqi Shen*, Dongsheng Li, and Shengling Chen
Predicting the Implicit and the Explicit Video Popularity in a User Generated Content Site with Enhanced Social Features
Computer Networks 2018, CCF B
 bibtex
bibtex

L. Luo, Y. Zang*, X. Wang, et al
Estimating Road Widths From Remote Sensing Images
Remote Sensing Letters
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{luo2018estimating,
title={Estimating Road Widths From Remote Sensing Images},
author={Luo, Lun and Zang, Yu and Wang, Xiaofang and Wang, Cheng and Li, Jonathan and Wu, Sheng and Liu, Yuelei},
journal={Remote Sensing Letters},
volume={9},
number={9},
pages={819--828},
year={2018},
publisher={Taylor \& Francis}
}

Chenglu Wen, Yan Xia, Yuhan Lian, Yudi Dai, Jinbin Tan, Cheng Wang, Jonathan Li
MOBILE LASER SCANNING SYSTEMS FOR GPS/GNSS-DENIED ENVIRONMENT MAPPING
International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{wen2018mobile,
title={MOBILE LASER SCANNING SYSTEMS FOR GPS/GNSS-DENIED ENVIRONMENT MAPPING},
author={Wen, Chenglu and Xia, Yan and Lian, Yuhan and Dai, Yudi and Tan, Jinbin and Wang, Cheng and Li, Jonathan},
journal={International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences},
volume={42},
pages={1},
year={2018}
}

Changbin You, Chenglu Wen*, Cheng Wang, Jonathan Li, Ayman Habib
Joint 2-D–3-D traffic sign landmark data set for geo-localization using mobile laser scanning data
IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems
 bibtex
bibtex
@ARTICLE{8478211, author={You, Changbin and Wen, Chenglu and Wang, Cheng and Li, Jonathan and Habib, Ayman}, journal={IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems}, title={Joint 2-D–3-D Traffic Sign Landmark Data Set for Geo-Localization Using Mobile Laser Scanning Data}, year={2019}, volume={20}, number={7}, pages={2550-2565}, doi={10.1109/TITS.2018.2868168}}

Cheng Wang, Shiwei Hou, Chenglu Wen*, Zheng Gong, Qing Li, Xiaotian Sun, Jonathan Li
Semantic line framework-based indoor building modeling using backpacked laser scanning point cloud
ISPRS journal of photogrammetry and remote sensing
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{WANG2018150,
title = {Semantic line framework-based indoor building modeling using backpacked laser scanning point cloud},
journal = {ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing},
volume = {143},
pages = {150-166},
year = {2018},
note = {ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing Theme Issue “Point Cloud Processing”},
issn = {0924-2716},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2018.03.025},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092427161830090X},
author = {Cheng Wang and Shiwei Hou and Chenglu Wen and Zheng Gong and Qing Li and Xiaotian Sun and Jonathan Li},
keywords = {Point clouds, Indoor modeling, Mobile laser scanning, Line framework extraction, Semantic labeling},
abstract = {Indoor building models are essential in many indoor applications. These models are composed of the primitives of the buildings, such as the ceilings, floors, walls, windows, and doors, but not the movable objects in the indoor spaces, such as furniture. This paper presents, for indoor environments, a novel semantic line framework-based modeling building method using backpacked laser scanning point cloud data. The proposed method first semantically labels the raw point clouds into the walls, ceiling, floor, and other objects. Then line structures are extracted from the labeled points to achieve an initial description of the building line framework. To optimize the detected line structures caused by furniture occlusion, a conditional Generative Adversarial Nets (cGAN) deep learning model is constructed. The line framework optimization model includes structure completion, extrusion removal, and regularization. The result of optimization is also derived from a quality evaluation of the point cloud. Thus, the data collection and building model representation become a united task-driven loop. The proposed method eventually outputs a semantic line framework model and provides a layout for the interior of the building. Experiments show that the proposed method effectively extracts the line framework from different indoor scenes.}
}

Q Fan, F Chen*, M Cheng, C Wang, J Li
A modified framework for ship detection from compact polarization SAR image
IGARSS 2018-2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium
 bibtex
bibtex
@inproceedings{fan2018modified,
title={A modified framework for ship detection from compact polarization SAR image},
author={Fan, Qiancong and Chen, Feng and Cheng, Ming and Wang, Cheng and Li, Jonathan},
booktitle={IGARSS 2018-2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium},
pages={3539--3542},
year={2018},
organization={IEEE}
}

C Chen, X Fan*, C Zheng, L Xiao, M Cheng, C Wang
Sdcae: Stack denoising convolutional autoencoder model for accident risk prediction via traffic big data
2018 Sixth International Conference on Advanced Cloud and Big Data (CBD)
 bibtex
bibtex
@inproceedings{chen2018sdcae,
title={Sdcae: Stack denoising convolutional autoencoder model for accident risk prediction via traffic big data},
author={Chen, Chao and Fan, Xiaoliang and Zheng, Chuanpan and Xiao, Lujing and Cheng, Ming and Wang, Cheng},
booktitle={2018 Sixth International Conference on Advanced Cloud and Big Data (CBD)},
pages={328--333},
year={2018},
organization={IEEE}
}

Adele Lu Jia, Siqi Shen*, Dongsheng Li, and Shengling Chen
Predicting the Implicit and the Explicit Video Popularity in a User Generated Content Site with Enhanced Social Features, Computer Networks
2018, CCF B
 bibtex
bibtex
312312
321312

Longbiao Chen, Jérémie Jakubowicz, Dingqi Yang, Daqing Zhang, Gang Pan
Fine-grained urban event detection and characterization based on tensor cofactorization
THMS
 bibtex
bibtex
@ARTICLE{7547355,
author={Chen, Longbiao and Jakubowicz, Jérémie and Yang, Dingqi and Zhang, Daqing and Pan, Gang},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Human-Machine Systems},
title={Fine-Grained Urban Event Detection and Characterization Based on Tensor Cofactorization},
year={2017},
volume={47},
number={3},
pages={380-391},
keywords={Event detection;Tensile stress;Data integration;Semantics;Global Positioning System;Urban planning;Event detection;tensor factorization;urban data},
doi={10.1109/THMS.2016.2596103}}

Ding, L. and Huang, H. and Zang, Y*
Image Quality Assessment Using Directional Anisotropy Structure Measurement
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{2017Image,
title={Image Quality Assessment Using Directional Anisotropy Structure Measurement},
author={ Ding, L. and Huang, H. and Zang, Y. },
journal={IEEE Transactions on Image Processing},
volume={26},
number={4},
pages={1799-1809},
year={2017},
}

Y. Zang*, C. Wang, Y. Yu, L. Luo, Y. Ke, J. Li.
Joint Enhancing Filtering for Road Network Extraction
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing
 bibtex
bibtex
null

Dongsheng Li, Wangxing Zhang, Siqi Shen, Yiming Zhang
SES-LSH: Shuffle-Efficient Locality Sensitive Hashing for Distributed Similarity Search
ICWS 2017, CCF B
 bibtex
bibtex

Y. Zang, C. Wang, Y. Yu, L. Luo, Y. Ke, J. Li
Joint Enhancing Filtering for Road Network Extraction
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{zang2016joint,
title={Joint enhancing filtering for road network extraction},
author={Zang, Yu and Wang, Cheng and Yu, Yao and Luo, Lun and Yang, Ke and Li, Jonathan},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing},
volume={55},
number={3},
pages={1511--1525},
year={2016},
publisher={IEEE}
}

D. Li, H. Huang, Y. Zang
Image Quality Assessment Using Directional Anisotropy Structure Measurement
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing
 bibtex
bibtex
@ARTICLE{7847359, author={Ding, Li and Huang, Hua and Zang, Yu}, journal={IEEE Transactions on Image Processing}, title={Image Quality Assessment Using Directional Anisotropy Structure Measurement}, year={2017}, volume={26}, number={4}, pages={1799-1809}, doi={10.1109/TIP.2017.2665972}}

Zheng Gong, Chenglu Wen*, Cheng Wang, Jonathan Li
A target-free automatic self-calibration approach for multibeam laser scanners
IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement
 bibtex
bibtex
@ARTICLE{8067639, author={Gong, Zheng and Wen, Chenglu and Wang, Cheng and Li, Jonathan}, journal={IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement}, title={A Target-Free Automatic Self-Calibration Approach for Multibeam Laser Scanners}, year={2018}, volume={67}, number={1}, pages={238-240}, doi={10.1109/TIM.2017.2757148}}

P Huang, M Cheng*, Y Chen, H Luo, C Wang, J Li*
Traffic sign occlusion detection using mobile laser scanning point clouds
IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{huang2017traffic,
title={Traffic sign occlusion detection using mobile laser scanning point clouds},
author={Huang, Pengdi and Cheng, Ming and Chen, Yiping and Luo, Huan and Wang, Cheng and Li, Jonathan},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems},
volume={18},
number={9},
pages={2364--2376},
year={2017},
publisher={IEEE}
}

P Huang, M Cheng*, Y Chen, D Zai, C Wang, J Li*
Solar potential analysis method using terrestrial laser scanning point clouds
IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{huang2017solar,
title={Solar potential analysis method using terrestrial laser scanning point clouds},
author={Huang, Pengdi and Cheng, Ming and Chen, Yiping and Zai, Dawei and Wang, Cheng and Li, Jonathan},
journal={IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing},
volume={10},
number={3},
pages={1221--1233},
year={2017},
publisher={IEEE}
}

D Zai, J Li*, Y Guo, M Cheng, Y Lin, H Luo, C Wang
3-D road boundary extraction from mobile laser scanning data via supervoxels and graph cuts
IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{zai20173,
title={3-D road boundary extraction from mobile laser scanning data via supervoxels and graph cuts},
author={Zai, Dawei and Li, Jonathan and Guo, Yulan and Cheng, Ming and Lin, Yangbin and Luo, Huan and Wang, Cheng},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems},
volume={19},
number={3},
pages={802--813},
year={2017},
publisher={IEEE}
}

X Zou, M Cheng*, C Wang, Y Xia, J Li
Tree classification in complex forest point clouds based on deep learning
IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{zou2017tree,
title={Tree classification in complex forest point clouds based on deep learning},
author={Zou, Xinhuai and Cheng, Ming and Wang, Cheng and Xia, Yan and Li, Jonathan},
journal={IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters},
volume={14},
number={12},
pages={2360--2364},
year={2017},
publisher={IEEE}
}

D Zai, J Li*, Y Guo, M Cheng, P Huang, X Cao, C Wang
Pairwise registration of TLS point clouds using covariance descriptors and a non-cooperative game
ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{zai2017pairwise,
title={Pairwise registration of TLS point clouds using covariance descriptors and a non-cooperative game},
author={Zai, Dawei and Li, Jonathan and Guo, Yulan and Cheng, Ming and Huang, Pengdi and Cao, Xiaofei and Wang, Cheng},
journal={ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing},
volume={134},
pages={15--29},
year={2017},
publisher={Elsevier}
}

Dongsheng Li, Wangxing Zhang, Siqi Shen, Yiming Zhang, SES-LSH
Shuffle-Efficient Locality Sensitive Hashing for Distributed Similarity Search
IEEE International Conference on Web Services (ICWS), 2017, CCF B
 bibtex
bibtex
312312
321312

Longbiao Chen, Daqing Zhang, Leye Wang, Dingqi Yang, Xiaojuan Ma, Shijian Li, Zhaohui Wu, Gang Pan, Thi-Mai-Trang Nguyen, Jérémie Jakubowicz
Dynamic cluster-based over-demand prediction in bike sharing systems
UbiComp
 bibtex
bibtex
@inproceedings{10.1145/2971648.2971652,
author = {Chen, Longbiao and Zhang, Daqing and Wang, Leye and Yang, Dingqi and Ma, Xiaojuan and Li, Shijian and Wu, Zhaohui and Pan, Gang and Nguyen, Thi-Mai-Trang and Jakubowicz, J\'{e}r\'{e}mie},
title = {Dynamic cluster-based over-demand prediction in bike sharing systems},
year = {2016},
isbn = {9781450344616},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/2971648.2971652},
doi = {10.1145/2971648.2971652},
abstract = {Bike sharing is booming globally as a green transportation mode, but the occurrence of over-demand stations that have no bikes or docks available greatly affects user experiences. Directly predicting individual over-demand stations to carry out preventive measures is difficult, since the bike usage pattern of a station is highly dynamic and context dependent. In addition, the fact that bike usage pattern is affected not only by common contextual factors (e.g., time and weather) but also by opportunistic contextual factors (e.g., social and traffic events) poses a great challenge. To address these issues, we propose a dynamic cluster-based framework for over-demand prediction. Depending on the context, we construct a weighted correlation network to model the relationship among bike stations, and dynamically group neighboring stations with similar bike usage patterns into clusters. We then adopt Monte Carlo simulation to predict the over-demand probability of each cluster. Evaluation results using real-world data from New York City and Washington, D.C. show that our framework accurately predicts over-demand clusters and outperforms the baseline methods significantly.},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 2016 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing},
pages = {841–852},
numpages = {12},
keywords = {urban data, over-demand prediction, bike sharing system},
location = {Heidelberg, Germany},
series = {UbiComp '16}
}

Longbiao Chen, Daqing Zhang, Xiaojuan Ma, Leye Wang, Shijian Li, Zhaohui Wu, Gang Pan
Container port performance measurement and comparison leveraging ship GPS traces and maritime open data
TITS
 bibtex
bibtex
@ARTICLE{7345574,
author={Chen, Longbiao and Zhang, Daqing and Ma, Xiaojuan and Wang, Leye and Li, Shijian and Wu, Zhaohui and Pan, Gang},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems},
title={Container Port Performance Measurement and Comparison Leveraging Ship GPS Traces and Maritime Open Data},
year={2016},
volume={17},
number={5},
pages={1227-1242},
keywords={Containers;Marine vehicles;Ports (Computers);Global Positioning System;Throughput;Productivity;Measurement;Container port;GPS trace;open data;intelligent transportation system (ITS);urban computing;Container port;GPS trace;open data;intelligent transportation system (ITS);urban computing},
doi={10.1109/TITS.2015.2498409}}

Y. Zang, C. Wang*, L. Cao, Y. Yu, J. Li.
Road Network Extraction via Aperiodic Directional Structure Measurement
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing
 bibtex
bibtex
null

Adele Lu Jia, Siqi Shen*, Dick Epema, and Alexandru Iosup
When game becomes life: The creators and the spectators of online game replays and live streaming
TOMM 2016, CCF B
 bibtex
bibtex

F Huang, C Wen*, H Luo, M Cheng, C Wang, J Li
Local quality assessment of point clouds for indoor mobile mapping
Neurocomputing
 bibtex
bibtex

Y. Zang, C. Wang, L. Cao, Y. Yu, J. Li
Road Network Extraction via Aperiodic Directional Structure Measurement
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{zang2016road,
title={Road network extraction via aperiodic directional structure measurement},
author={Zang, Yu and Wang, Cheng and Cao, Liujuan and Yu, Yao and Li, Jonathan},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing},
volume={54},
number={6},
pages={3322--3335},
year={2016},
publisher={IEEE}
}

X Guo, Y Chen, C Wang, M Cheng, C Wen, J Yu
Automatic shape-based target extraction for close-range photogrammetry
Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci.
 bibtex
bibtex
@inproceedings{guo2016automatic,
title={Automatic shape-based target extraction for close-range photogrammetry},
author={Guo, X and Chen, Y and Wang, C and Cheng, M and Wen, C and Yu, J},
booktitle={Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci.},
volume={41},
pages={583--587},
year={2016}
}

Fan Wu, Chenglu Wen, Yulan Guo, Jingjing Wang, Yongtao Yu, Cheng Wang, Jonathan Li
Rapid localization and extraction of street light poles in mobile LiDAR point clouds: A supervoxel-based approach
IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems
 bibtex
bibtex
@ARTICLE{7497465, author={Wu, Fan and Wen, Chenglu and Guo, Yulan and Wang, Jingjing and Yu, Yongtao and Wang, Cheng and Li, Jonathan}, journal={IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems}, title={Rapid Localization and Extraction of Street Light Poles in Mobile LiDAR Point Clouds: A Supervoxel-Based Approach}, year={2017}, volume={18}, number={2}, pages={292-305}, doi={10.1109/TITS.2016.2565698}}

Yongtao Yu, Jonathan Li, Chenglu Wen, Haiyan Guan, Huan Luo, Cheng Wang
Bag-of-visual-phrases and hierarchical deep models for traffic sign detection and recognition in mobile laser scanning data
ISPRS journal of photogrammetry and remote sensing
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{YU2016106,
title = {Bag-of-visual-phrases and hierarchical deep models for traffic sign detection and recognition in mobile laser scanning data},
journal = {ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing},
volume = {113},
pages = {106-123},
year = {2016},
issn = {0924-2716},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2016.01.005},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0924271616000198},
author = {Yongtao Yu and Jonathan Li and Chenglu Wen and Haiyan Guan and Huan Luo and Cheng Wang},
keywords = {Bag-of-visual-phrases, Deep Boltzmann machine (DBM), Mobile laser scanning (MLS), Point cloud, Traffic sign detection, Traffic sign recognition (TSR)},
abstract = {This paper presents a novel algorithm for detection and recognition of traffic signs in mobile laser scanning (MLS) data for intelligent transportation-related applications. The traffic sign detection task is accomplished based on 3-D point clouds by using bag-of-visual-phrases representations; whereas the recognition task is achieved based on 2-D images by using a Gaussian-Bernoulli deep Boltzmann machine-based hierarchical classifier. To exploit high-order feature encodings of feature regions, a deep Boltzmann machine-based feature encoder is constructed. For detecting traffic signs in 3-D point clouds, the proposed algorithm achieves an average recall, precision, quality, and F-score of 0.956, 0.946, 0.907, and 0.951, respectively, on the four selected MLS datasets. For on-image traffic sign recognition, a recognition accuracy of 97.54% is achieved by using the proposed hierarchical classifier. Comparative studies with the existing traffic sign detection and recognition methods demonstrate that our algorithm obtains promising, reliable, and high performance in both detecting traffic signs in 3-D point clouds and recognizing traffic signs on 2-D images.}
}

Haocheng Zhang, Jonathan Li*, Ming Cheng, Cheng Wang
Rapid Inspection of Pavement Markings Using Mobile LIDAR Point Clouds
ISPRS-International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{zhang2016rapid,
title={RAPID INSPECTION OF PAVEMENT MARKINGS USING MOBILE LIDAR POINT CLOUDS.},
author={Zhang, Haocheng and Li, Jonathan and Cheng, Ming and Wang, Cheng},
journal={International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing \& Spatial Information Sciences},
volume={41},
year={2016}
}

F Huang, C Wen*, H Luo, M Cheng, C Wang, J Li
Local quality assessment of point clouds for indoor mobile mapping
Neurocomputing
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{huang2016local,
title={Local quality assessment of point clouds for indoor mobile mapping},
author={Huang, Fangfang and Wen, Chenglu and Luo, Huan and Cheng, Ming and Wang, Cheng and Li, Jonathan},
journal={Neurocomputing},
volume={196},
pages={59--69},
year={2016},
publisher={Elsevier}
}

Ziyi Chen, Cheng Wang, Chenglu Wen, Xiuhua Teng, Yiping Chen, Haiyan Guan, Huan Luo, Liujuan Cao, Jonathan Li
Vehicle detection in high-resolution aerial images via sparse representation and superpixels
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing
 bibtex
bibtex
@ARTICLE{7163593, author={Chen, Ziyi and Wang, Cheng and Wen, Chenglu and Teng, Xiuhua and Chen, Yiping and Guan, Haiyan and Luo, Huan and Cao, Liujuan and Li, Jonathan}, journal={IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing}, title={Vehicle Detection in High-Resolution Aerial Images via Sparse Representation and Superpixels}, year={2016}, volume={54}, number={1}, pages={103-116}, doi={10.1109/TGRS.2015.2451002}}

M Cheng, H Zhang, C Wang, J Li*
Extraction and classification of road markings using mobile laser scanning point clouds
IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{cheng2016extraction,
title={Extraction and classification of road markings using mobile laser scanning point clouds},
author={Cheng, Ming and Zhang, Haocheng and Wang, Cheng and Li, Jonathan},
journal={IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing},
volume={10},
number={3},
pages={1182--1196},
year={2016},
publisher={IEEE}
}

L Cao, Q Jiang, M Cheng*, C Wang
Robust vehicle detection by combining deep features with exemplar classification
Neurocomputing
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{cao2016robust,
title={Robust vehicle detection by combining deep features with exemplar classification},
author={Cao, Liujuan and Jiang, Qilin and Cheng, Ming and Wang, Cheng},
journal={Neurocomputing},
volume={215},
pages={225--231},
year={2016},
publisher={Elsevier}
}

Longbiao Chen, Daqing Zhang, Gang Pan, Xiaojuan Ma, Dingqi Yang, Kostadin Kushlev, Wangsheng Zhang, Shijian Li
Bike sharing station placement leveraging heterogeneous urban open data
UbiComp
 bibtex
bibtex
@inproceedings{10.1145/2750858.2804291,
author = {Chen, Longbiao and Zhang, Daqing and Pan, Gang and Ma, Xiaojuan and Yang, Dingqi and Kushlev, Kostadin and Zhang, Wangsheng and Li, Shijian},
title = {Bike sharing station placement leveraging heterogeneous urban open data},
year = {2015},
isbn = {9781450335744},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/2750858.2804291},
doi = {10.1145/2750858.2804291},
abstract = {Bike sharing systems have been deployed in many cities to promote green transportation and a healthy lifestyle. One of the key factors for maximizing the utility of such systems is placing bike stations at locations that can best meet users' trip demand. Traditionally, urban planners rely on dedicated surveys to understand the local bike trip demand, which is costly in time and labor, especially when they need to compare many possible places. In this paper, we formulate the bike station placement issue as a bike trip demand prediction problem. We propose a semi-supervised feature selection method to extract customized features from the highly variant, heterogeneous urban open data to predict bike trip demand. Evaluation using real-world open data from Washington, D.C. and Hangzhou shows that our method can be applied to different cities to effectively recommend places with higher potential bike trip demand for placing future bike stations.},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 2015 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing},
pages = {571–575},
numpages = {5},
keywords = {urban computing, open data, bike sharing system},
location = {Osaka, Japan},
series = {UbiComp '15}
}

Y. Zang, H. Huang*, L. Zhang.
Guided Adaptive Image Smoothing via Directional Anisotropic Structure Measurement
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics
 bibtex
bibtex
null

Adele Lu Jia, Siqi Shen*, Ruud van de Bovenkamp, Alexandru Iosup, Fernando Kuipers, and Dick Epema
Socializing by Gaming: Revealing Social Relationships in Multiplayer Online Games
TKDD 2015, CCF B
 bibtex
bibtex

Siqi Shen, Shunyun Hu, Alexandru Iosup, and Dick Epema
The Area of Simulation Mechanism and Architecture for Multi-Avatar Virtual Environments
TOMM 2015, CCF B
 bibtex
bibtex

Marcus Martens, Siqi Shen, Alexandru Iosup, and Fernando Kuipers
Toxicity Detection in Multiplayer Online Games
NetGames 2015, BEST Paper
 bibtex
bibtex

Siqi Shen, Alexandru Iosup, Assaf Israel, Walfredo Cirne, Danny Raz, and Dick Epema
An Availability-on-Demand Mechanism for Datacenters
CCGrid 2015, CCF C
 bibtex
bibtex

Siqi Shen, Vincent van Beek, and Alexandru Iosup
Statistical Characterization of Business-Critical Workloads Hosted in Cloud Datacenters
CCGrid 2015, CCF C
 bibtex
bibtex

Zhipeng Cai, Cheng Wang, Chenglu Wen, Jonathan Li
Occluded Boundary Detection for Small-Footprint Groundborne LIDAR Point Cloud Guided by Last Echo
IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters
 bibtex
bibtex
@ARTICLE{7226818, author={Cai, Zhipeng and Wang, Cheng and Wen, Chenglu and Li, Jonathan}, journal={IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters}, title={Occluded Boundary Detection for Small-Footprint Groundborne LIDAR Point Cloud Guided by Last Echo}, year={2015}, volume={12}, number={11}, pages={2272-2276}, doi={10.1109/LGRS.2015.2466811}}

Siqi Shen, Shunyun Hu, Alexandru Iosup, and Dick Epema
The Area of Simulation Mechanism and Architecture for Multi-Avatar Virtual Environments
ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications and Applications (TOMM), 2015, CCF B
 bibtex
bibtex
312312
321312

Adele Lu Jia, Siqi Shen*, Ruud van de Bovenkamp, Alexandru Iosup, Fernando Kuipers, and Dick Epema
Socializing by Gaming: Revealing Social Relationships in Multiplayer Online Games
ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discovery from Data (TKDD), 2015, CCF B
 bibtex
bibtex
312312
321312

Longbiao Chen, Daqing Zhang, Gang Pan, Leye Wang, Xiaojuan Ma, Chao Chen, Shijian Li
Container throughput estimation leveraging ship GPS traces and open data
UbiComp
 bibtex
bibtex
@inproceedings{10.1145/2632048.2632050,
author = {Chen, Longbiao and Zhang, Daqing and Pan, Gang and Wang, Leye and Ma, Xiaojuan and Chen, Chao and Li, Shijian},
title = {Container throughput estimation leveraging ship GPS traces and open data},
year = {2014},
isbn = {9781450329682},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/2632048.2632050},
doi = {10.1145/2632048.2632050},
abstract = {Traditionally, the port container throughput, a crucial measurement of regional economic development, was manually collected by port authorities. This requires a large amount of human effort and often delays publication of this important figure. In this paper, by leveraging ubiquitous positioning techniques and open data, we propose a two-phase approach to estimation of port container throughput in real-time. First, we obtain the number of container ships arriving at berth by analyzing the ships' GPS traces. Then we estimate the throughput of each ship, in terms of number of containers transshipped, by considering the ship's berthing time, capacity, length, breadth, and crane operation performance, as extracted from different data sources. Evaluation results using real-world datasets from Hong Kong and Singapore show that the proposed approach not only estimates the container throughput quite accurately, but also outperforms the baseline method significantly.},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 2014 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing},
pages = {847–851},
numpages = {5},
keywords = {AIS trace, container throughput estimation, open data},
location = {Seattle, Washington},
series = {UbiComp '14}
}

Zang Y , Huang H* , Zhang L
Efficient Structure-Aware Image Smoothingby Local Extrema on Space-Filling Curve
IEEE Transactions on Visualization & Computer Graphics
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{2014Efficient,
title={Efficient Structure-Aware Image Smoothingby Local Extrema on Space-Filling Curve},
author={ Zang, Yu and Huang, Hua and Zhang, Lei },
journal={IEEE Transactions on Visualization & Computer Graphics},
volume={20},
number={9},
pages={1253-1265},
year={2014},
}

Siqi Shen, Niels Brouwers, Alexandru Iosup, and Dick Epema
Characterization of Human Mobility in Networked Virtual Environments
NOSSDAV 2014, CCF B
 bibtex
bibtex

Yunhua Deng, Siqi Shen, Zhe Huang, Alexandru Iosup, and Rynson Lau
Dynamic Resource Management in Cloud-based Distributed Virtual Environment
ACM Multimedia 2014, CCF A
 bibtex
bibtex

Siqi Shen and Alexandru Iosup
Modeling Avatar Mobility of Networked Virtual Environments
MMVE 2014
 bibtex
bibtex

Y. Zang, H. Huang, L. Zhang
Efficient Image Filtering via Local Extrema on Space Filling Curve
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{zang2014efficient,
title={Efficient structure-aware image smoothingby local extrema on space-filling curve},
author={Zang, Yu and Huang, Hua and Zhang, Lei},
journal={IEEE transactions on visualization and computer graphics},
volume={20},
number={9},
pages={1253--1265},
year={2014},
publisher={IEEE}
}

Y. Zang, H. Huang, C. Li
Image stylization via artistic vision
The Visual Computer
 bibtex
bibtex
@article{zang2014artistic,
title={Artistic preprocessing for painterly rendering and image stylization},
author={Zang, Yu and Huang, Hua and Li, Chen-Feng},
journal={The Visual Computer},
volume={30},
number={9},
pages={969--979},
year={2014},
publisher={Springer}
}

Qingyuan Zhu, Jian Yi, Shiyue Sheng, Chenglu Wen, Huosheng Hu
A computer-aided modeling and measurement system for environmental thermal comfort sensing
IEEE transactions on instrumentation and measurement
 bibtex
bibtex
@ARTICLE{6880371, author={Zhu, Qingyuan and Yi, Jian and Sheng, Shiyue and Wen, Chenglu and Hu, Huosheng}, journal={IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement}, title={A Computer-Aided Modeling and Measurement System for Environmental Thermal Comfort Sensing}, year={2015}, volume={64}, number={2}, pages={478-486}, doi={10.1109/TIM.2014.2345922}}