Professor 教授,博士生导师,国家高层次青年人才
clwen@xmu.edu.cn
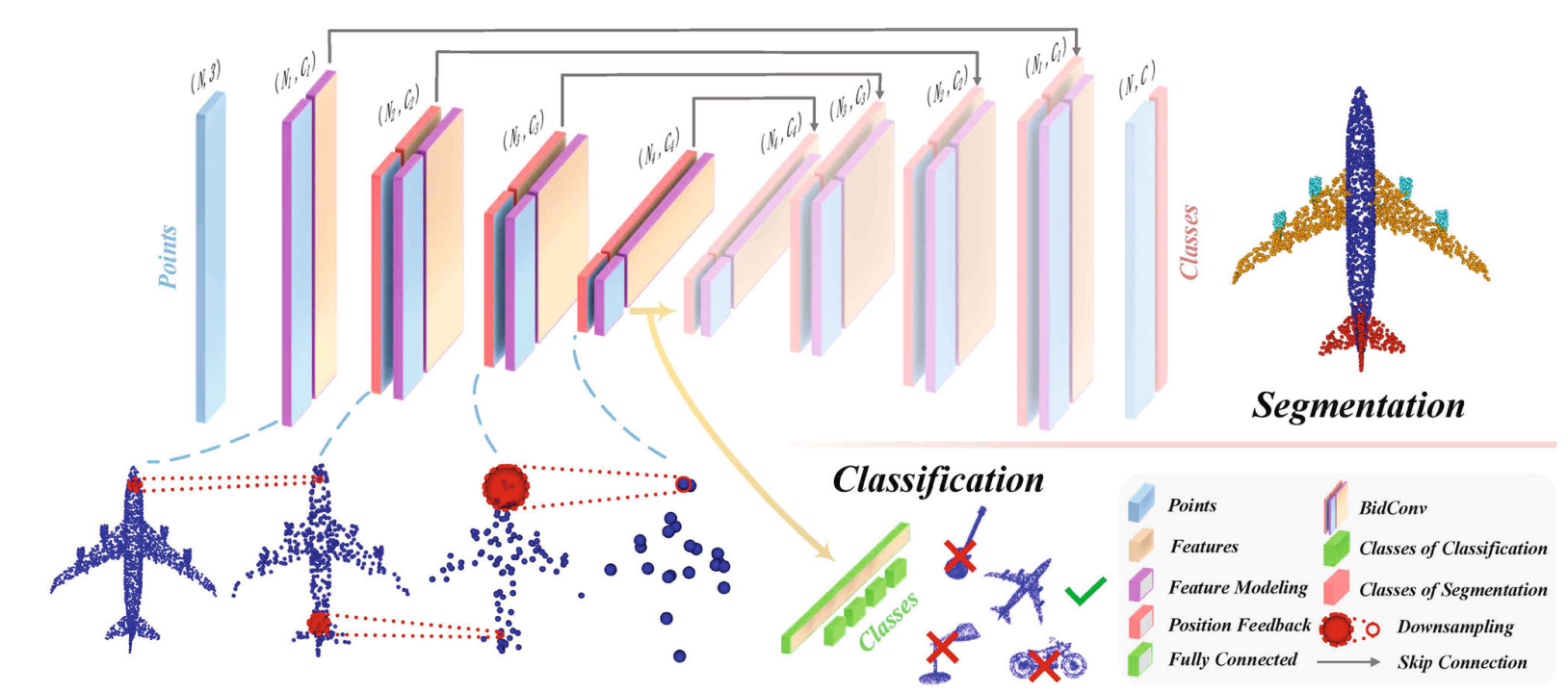
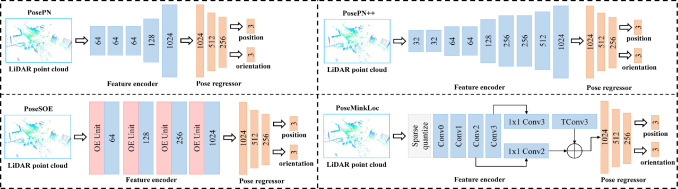
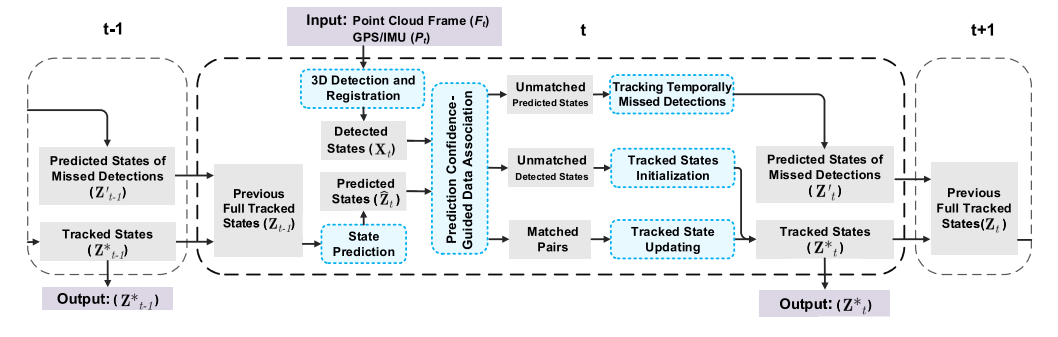
人工智能系教授,福建省智慧城市感知与计算重点实验室副主任。主要从事三维视觉、点云智能处理、具身智能主动感知方面研究。主持国家自然科学基金项目三项等国家级项目。成果发表在CVPR、ICCV、ECCV、NeurIPS等人工智能国际会议,和IEEE TPAMI、IEEE TGRS、IEEE TITS、ISPRS JPRS等期刊上。获国际摄影测量与遥感学会ISPRS Otto von Gruber奖(www.isprs.org/society/awards/gruber.aspx, 2022),福建省高等教育教学成果奖特等奖(2022),福建省科技进步奖二等奖(2021,2022),中国激光雷达青年科技奖(2020),福建省自然科学优秀学术论文奖二等奖(2022),CCF智能汽车青年激励计划(2024)。担任IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems期刊Senior Editor,IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters期刊Associate Editor,ISPRS I/2移动测图技术工作组联合主席,CSIG 厦门会员活动中心执委会主席。为CCF智能汽车分会执行委员,CSIG三维视觉专委会委员,CNISDE激光雷达专委会委员等。
主持的科研项目
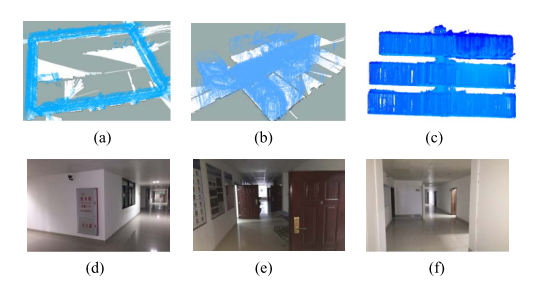
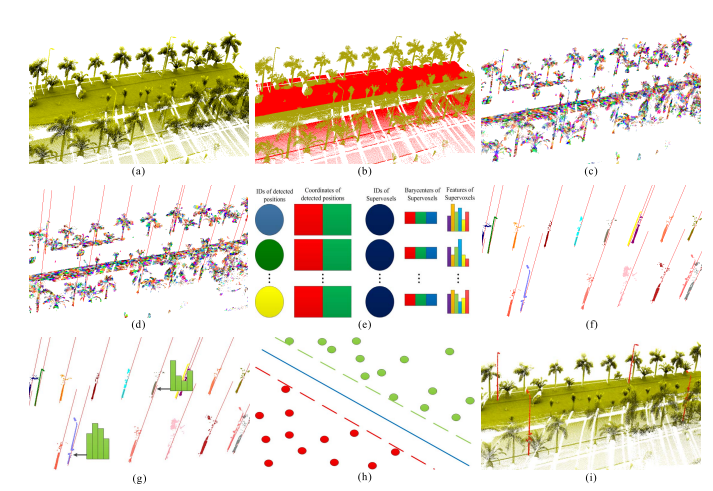
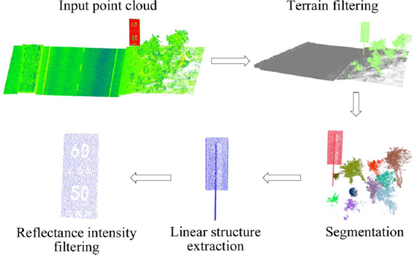
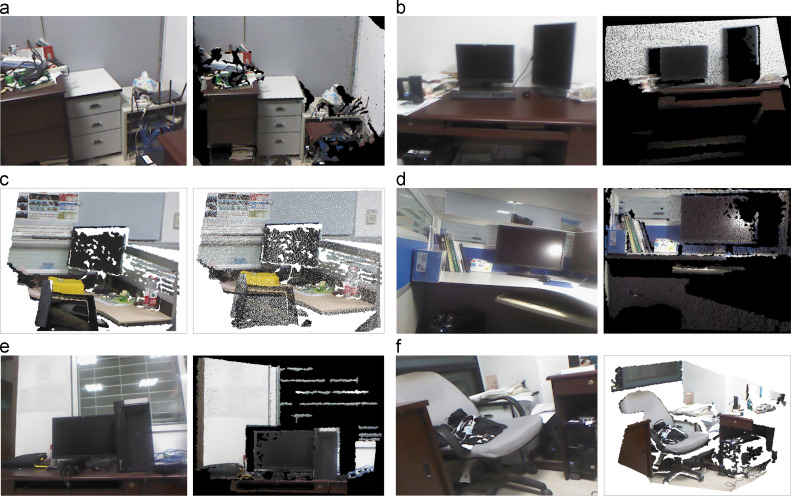
国家自然科学基金项目,面向城市动态场景三维感知的点云序列弱监督学习,2022-2025
国家自然科学基金项目,联合可测点云/多视角图像的大规模对象标记数据集生成,2018-2021
国家自然科学基金项目,室内移动三维测图点云数据的多元质量评价与修补,2015-2017
国家重点研发计划青年科学家项目,多平台多模态点云大数据智能处理关键技术与软件(任务),2022-2024
Dr. Chenglu Wen is a Professor at the Department of Artificial Intelligence at Xiamen University. She was the deputy head of the Department of Artificial Intelligence. She is mainly engaged in the research of 3D scene perception and understanding, LiDAR point cloud processing, and 3D vision. She has been granted 3 National Natural Science Foundation of China projects. She has published over 100 papers and authorized over ten invention patents. She received the 2022 ISPRS Otto von Gruber Award (www.isprs.org/society/awards/gruber.aspx), the 2020 China LiDAR Youth Science and Technology Award, and Best Paper of the 2017 International Mobile Mapping Technology Conference. She serves as the Senior Editor of IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, and Associate Editor of IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters. She is also the co-chair of ISPRS working group I/2 Mobile Mapping Technology (2022-2026).
News
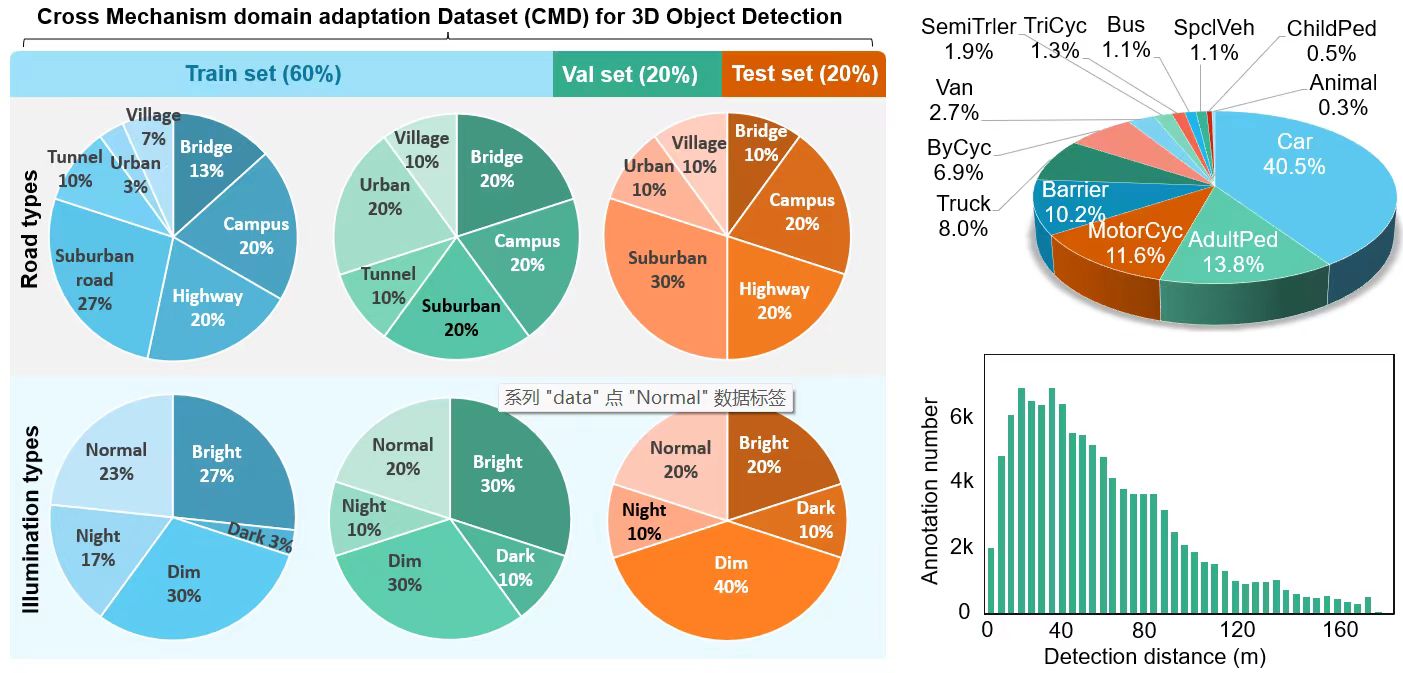
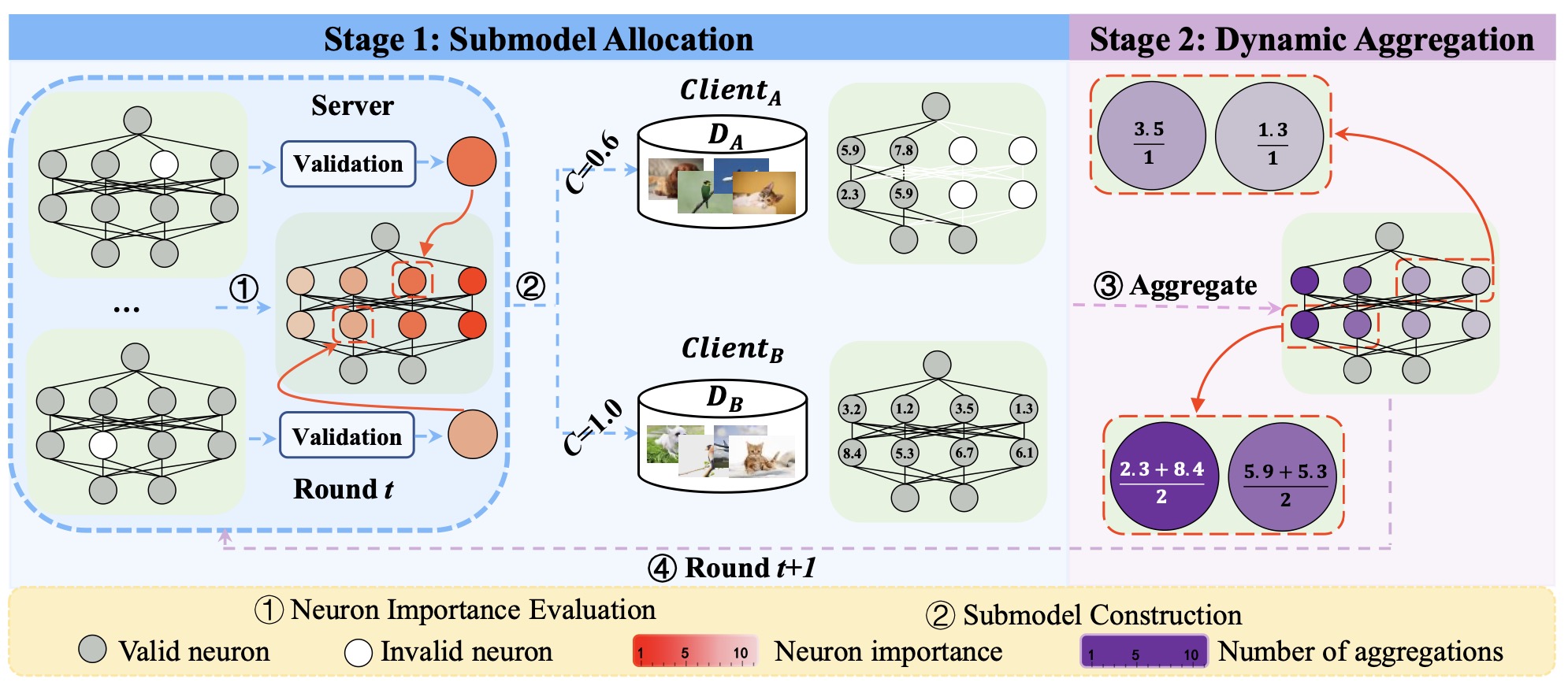
09/2024, two papers are accepted to NeurIPS 2024
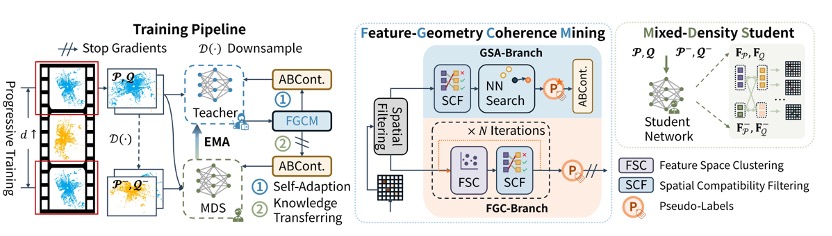
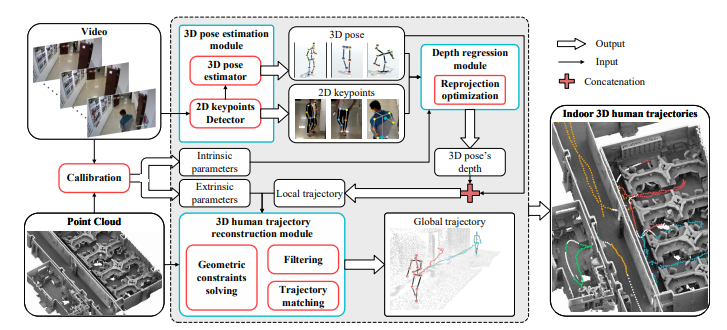
09/2024, our HiSC4D paper is accepted to IEEE TPAMI
07/2024, one paper is accepted to ECCV 2024
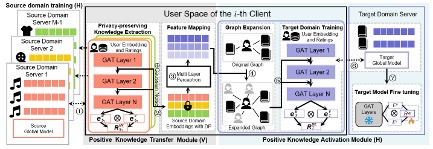
02/2024, five papers are accepted to CVPR 2024
12/2023, two papers are accepted to AAAI 2024
07/2023, one paper is accepted to ICCV 2023
02/2023, four papers are accepted to CVPR 2023
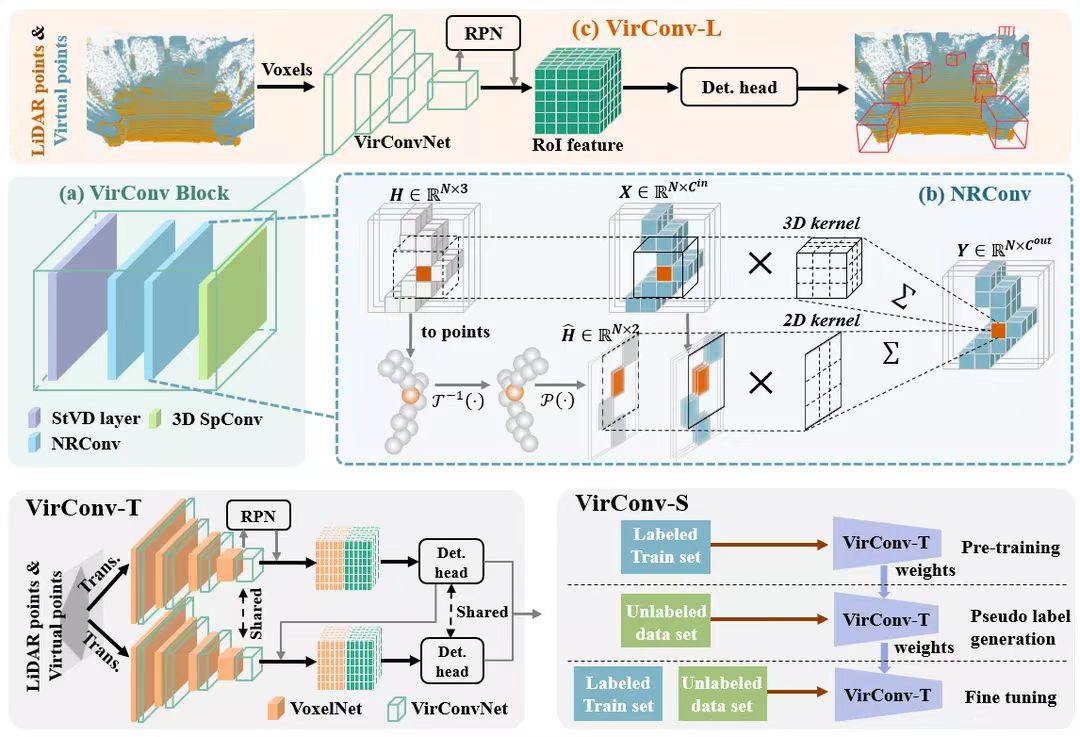
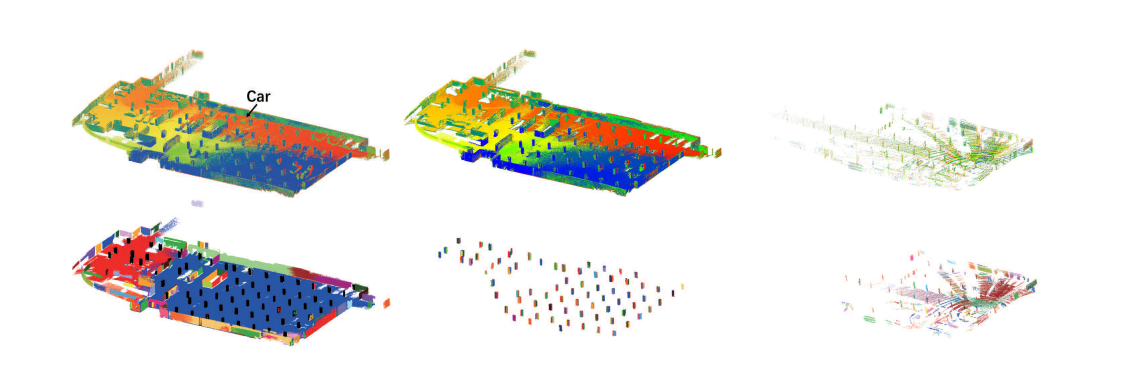
11/2022, our VirConv-S method ranks No.1(car) on the KITTI 2D, 3D and BEV detection leaderboard
11/2022, our VirConvTrack ranks No.1(car) on the KITTI tracking leaderboard
11/2022, our 3D object detection paper TED is accepted to AAAI 2023
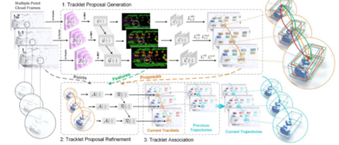
09/2022, our CasTrack ranks No.1(car) on the KITTI tracking leaderboard
06/2022, receive ISPRS Otto von Gruber Award
05/2022, our TED method ranks No.1(car) on the KITTI 3D detection leaderboard (until 11/2022)
05/2022, our CasA++ method ranks No.1(ped. and cyc.)/No.2(car) on the KITTI 3D detection leaderboard
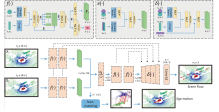
03/2022, two Lidar motion capture papers are accepted to CVPR 2022
04/2021, two papers are accepted to IJCAI 2021
01/2021, our PC-TCNN ranks No.1(car) on the KITTI tracking leaderboard
11/2020, I receive CNISDE Lidar Youth Science and Technology Award
06/2020, our paper “road scene labeling” reached ESI highly cited paper
11/2019, our paper “Point2Node” is accepted to AAAI 2020 as Oral Presentation
02/2019, two papers are accepted to CVPR 2019